Piecewise Definite integration - Practice Questions & MCQ
Quick Facts
-
Piecewise Definite integration is considered one the most difficult concept.
-
44 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
Choose the correct option
The value of $\int_{0}^{\pi}|\cos x|^3dx$ is :
The value of the integral
$\int_{-\pi/2}^{\pi/2}\frac{\sin^{2}x}{1+e^{x}}dx$
is
JEE Main 2026: Result OUT; Check Now | Final Answer Key Link
JEE Main 2026 Tools: College Predictor
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Link | Foreign Universities in India
Concepts Covered - 1
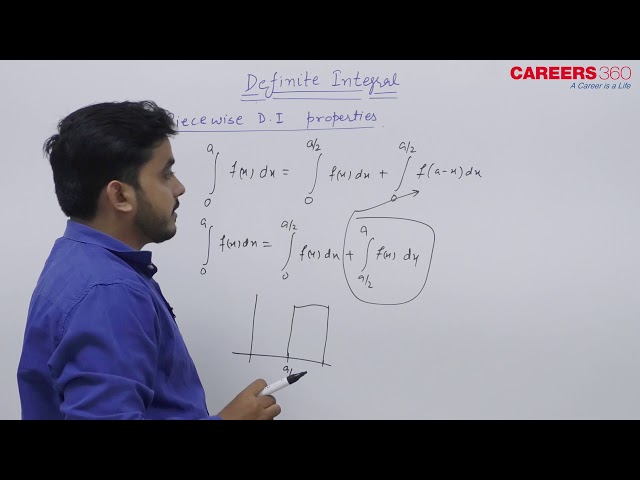
Property 5
$
\int_{\mathrm{a}}^{\mathrm{b}} \mathbf{f}(\mathrm{x}) \mathrm{d} \mathbf{x}=\int_{\mathrm{a}}^{\mathrm{c}} \mathbf{f}(\mathrm{x}) \mathrm{d} \mathbf{x}+\int_{\mathbf{c}}^{\mathrm{b}} \mathbf{f}(\mathbf{x}) \mathrm{dx} \text { where } c \in \mathbb{R}
$
This property is useful when the function is in the form of piecewise or discontinuous or non-differentiable at $x=c$ in $(a, b)$.
Let
$
\begin{aligned}
& \frac{d}{d x}(F(x))=f(x) \\
& \begin{aligned}
& \int_a^c f(x) d x+\int_c^b f(x) d x \\
& \quad=\left.F(x)\right|_a ^c+\left.F(x)\right|_c ^b \\
&=F(c)-F(a)+F(b)-F(c) \\
& \quad=F(b)-F(a) \\
& \quad=\int_a^b f(x) d x
\end{aligned}
\end{aligned}
$
$
\therefore \quad \int_a^c f(x) d x+\int_c^b f(x) d x
$
The above property can also be generalized into the following form
$
\int_a^b f(x) d x=\int_a^{c_1} f(x) d x+\int_{c_1}^{c_2} f(x) d x+\ldots+\int_{c_n}^b f(x) d x
$
where, $\quad a<c_1<c_2<\ldots<c_{n-1}<c_n<b$.
Property 6
$
\int_0^a f(x) d x=\int_0^{a / 2} f(x) d x+\int_0^{a / 2} f(a-x) d x
$
Proof:
From the previous property,
$
\int_0^a f(x) d x=\int_0^{a / 2} f(x) d x+\int_{a / 2}^a f(x) d x
$
Put $x=a-t \Rightarrow d x=-d t$ in the second integral, when $x=a / 2$, then $t=a / 2$ and when $x=a$, then $t=0$
$
\therefore \quad \begin{aligned}
\int_0^a f(x) d x & =\int_0^{a / 2} f(x) d x+\int_{a / 2}^0 f(a-t)(-d t) \\
& =\int_0^{\mathrm{a} / 2} \mathrm{f}(\mathrm{x}) \mathrm{dx}+\int_0^{\mathrm{a} / 2} \mathrm{f}(\mathrm{a}-\mathrm{t}) \mathrm{dt} \\
\int_0^a f(x) d x & =\int_0^{a / 2} f(x) d x+\int_0^{a / 2} f(a-x) d x
\end{aligned}
$
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"