Integration of Irrational Algebraic Function - Practice Questions & MCQ
Quick Facts
-
17 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
$\int\frac{e^{5 \log_{e}x}- e^{4 \log_{e}x}}{e^{3 \log_{e}x}-e^{2 \log_{e}x}}.dx$
is equal to ?
Concepts Covered - 4
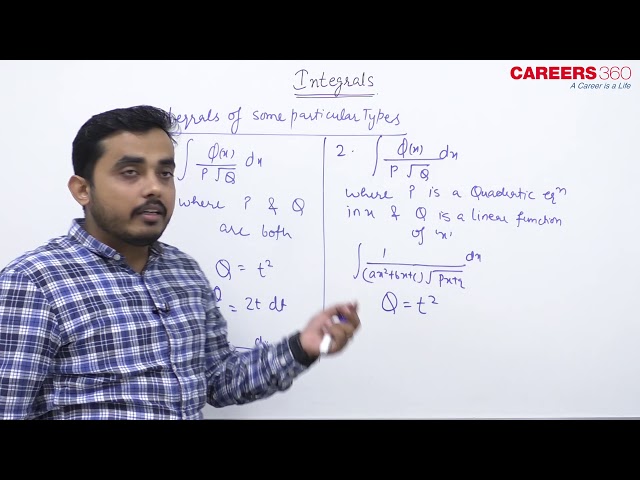
(a) Integrals of the Form
(i) $\int \frac{1}{(a x+b) \sqrt{p x+q}} d x$
(ii) $\int \frac{a x+b}{\sqrt{p x+q}} d x$
(iii) $\int \frac{\sqrt{p x+q}}{a x+b} d x$
(iv) $\int \frac{1}{\left(a x^2+b x+c\right) \sqrt{p x+q}} d x$
To evaluate this type of integrals, put px + q = t2
Illustration
Evaluate: $\int \frac{\mathrm{dx}}{(\mathrm{x}+1) \sqrt{\mathrm{x}+2}}$
Let $\mathrm{I}=\int \frac{d x}{(x+1) \sqrt{x+2}}$
Substitute: $x+2=t^2 \quad \Rightarrow \quad d x=2 t d t$
$
\begin{aligned}
& \Rightarrow \int \frac{d x}{x+1(\sqrt{x+2})}=\int \frac{2 t d t}{\left(t^2-1\right) \sqrt{t^2}}=2 \int \frac{d t}{t^2-1} \\
& =\frac{2}{2} \log \left|\frac{t-1}{t+1}\right|+C=\log \left|\frac{\sqrt{x+2}-1}{\sqrt{x+2+1}}\right|+C
\end{aligned}
$
(b) Integrals of the Form
(i) $\int \frac{1}{(p x+q) \sqrt{a x^2+b x+c}} d x$
To evaluate this type of integral, put $p x+q=1 / t$
(c) Integrals of the Form
(i) $\int \frac{1}{\left(\mathrm{ax}^2+\mathrm{b}\right) \sqrt{\mathrm{px}^2+\mathrm{q}}} d x$
To evaluate this type of integral, put $\mathrm{x}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{t}}$
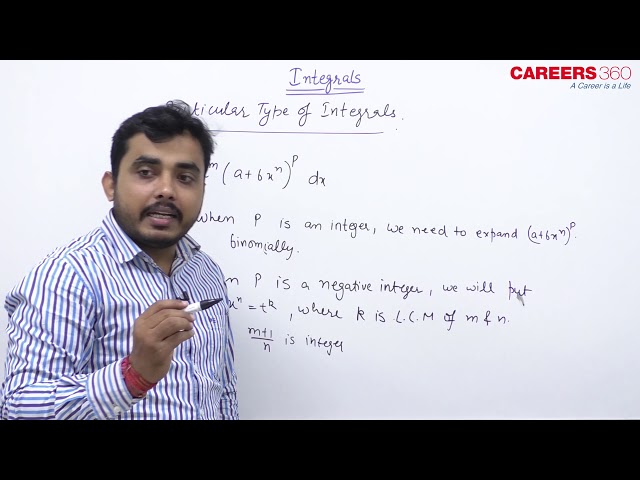
Integrals of the Form $\int x^m\left(a+b x^n\right)^p d x$
Working Rule:
Case I : If $P \in N$, expand using binomial and integrate.
Case II : If $P \in I^{-}$(ie, negative integer), write $x=t^k$ where $k$ is the LCM of $m$ and $n$.
Case III : If $\frac{m+1}{n}$ is an integer and $P \leftrightarrow$ fraction, put $\left(a+b x^n\right)=t^k$ where $k$ is denominator of the fraction $P$.
Case IV: If $\left(\frac{m+1}{n}+P\right)$ is an integer and $P \in$ fraction, $\operatorname{put}\left(a+b x^n\right)=t^k x^n$, where $k$ is denominator of the fraction $P$.
Integration of the form $\int \mathbf{f}\left(\mathbf{x}, \sqrt{\mathbf{a x}^2+\mathbf{b x}+\mathbf{c}}\right) \mathrm{dx}$ can be solved using one of the Euler's substitutions.
(i) $\sqrt{a x^2+b x+c}=t \pm x \sqrt{a}$, if $a>0$
(ii) $\sqrt{a x^2+b x+c}=t x+\sqrt{c}$, if $c>0$
(iii) $\sqrt{a x^2+b x+c}=(x-\alpha) t$, If $\alpha$ is real root of $a x^2+b x+c$.
Illustration
The value of the integral, $I=\int \frac{d x}{1+\sqrt{\mathrm{x}^2+2 \mathrm{x}+2}}$ is
Here $\mathrm{a}=1>0$, therefore make the substitution $\sqrt{x^2+2 x+2}=t-x$
Squaring both sides of this equality and reducing the similar terms, we get
$
\begin{aligned}
& x^2+2 x+2=(t-x)^2 \\
& x^2+2 x+2=t^2-2 t x+x^2 \\
& 2 x+2 t x=t^2-2 \\
& \Rightarrow \quad x=\frac{t^2-2}{2(1+t)} \Rightarrow d x=\frac{t^2+2 t+2}{2(1+t)^2} d t \\
& \quad 1+\sqrt{\mathrm{x}^2+2 \mathrm{x}+2}=1+\mathrm{t}-\frac{\mathrm{t}^2-2}{2(1+\mathrm{t})}=\frac{\mathrm{t}^2+4 \mathrm{t}+4}{2(1+\mathrm{t})^2}
\end{aligned}
$
Substituting into the integral, we get
$
I=\int \frac{2(1+t)\left(t^2+2 t+2\right)}{\left(t^2+4 t+4\right) 2(1+t)^2} d t=\int \frac{\left(t^2+2 t+2\right) d t}{(1+t)(1+2)^2}
$
Using the partial fraction,
$
\frac{t^2+2 t+2}{(t+1)(t+2)^2}=\frac{A}{t+1}+\frac{B}{t+2}+\frac{C}{(t+2)^2}
$
we get $\mathrm{A}=1, \mathrm{~B}=0$ and $\mathrm{C}=-2$
$
\frac{t^2+2 t+2}{(t+1)(t+2)^2}=\frac{1}{t+1}-\frac{2}{(t+2)^2}
$
Hence,
$
\begin{aligned}
\int \frac{\mathrm{t}^2+2 \mathrm{t}+2}{(1+\mathrm{t})(1+2)^2} \mathrm{dt} & =\int \frac{\mathrm{dt}}{\mathrm{t}+1}-2 \int \frac{\mathrm{dt}}{(\mathrm{t}+2)^2} \\
& =\ln |\mathrm{t}+1|+\frac{2}{\mathrm{t}+2}+\mathrm{C}
\end{aligned}
$
Now, put the value of $t$ in terms of $x$
$
I=\ln \left(x+1+\sqrt{x^2+2 x+2}\right)+\frac{2}{x+2+\sqrt{x^2+2 x+2}}+C
$
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"