Homogeneous Equations in Two Variables - Practice Questions & MCQ
Quick Facts
-
13 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
If the slope of one of the lines represented by $ax^{2}+10xy+y^{2}= 0$ is four times the slope of the other line, then the value of 'a' is
The pair of straight lines $x^2-4 x y+y^2=0$ together with the line $x+y+4 \sqrt{6}=0$ form a triangle which is :
Concepts Covered - 2
Homogeneous Equations in Two Variables
Homogeneous equations are those equations where each term has the same degree of variable terms.
The equation $a x^2+2 h x y+b y^2=0$ is a homogeneous equation of second degree.
It always represents two straight lines passing through the origin.
The given equation is :
$
a x^2+2 h x y+b y^2=0
$
Divide the equation by $x^2$
$
\Rightarrow \quad a+2 h\left(\frac{y}{x}\right)+b\left(\frac{y^2}{x^2}\right)=0
$
now put $\frac{y}{x}=m$
$
\Rightarrow \quad \mathrm{a}+2 \mathrm{~h}(\mathrm{~m})+\mathrm{b}\left(\mathrm{~m}^2\right)=0 \quad \ldots \text { (ii) }
$
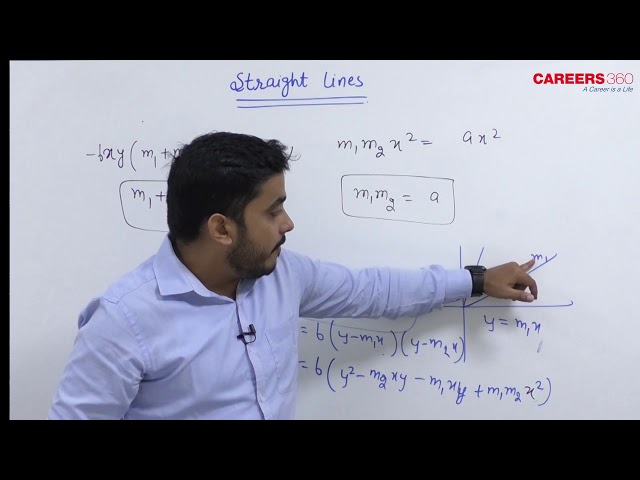
If $\mathrm{m}_1$ and $\mathrm{m}_2$ are roots, then
$
\mathrm{m}_1+\mathrm{m}_2=-\frac{2 \mathrm{~h}}{\mathrm{~b}}
$
amd, $\quad \mathrm{m}_1 \mathrm{~m}_2=\frac{\mathrm{b}}{\mathrm{a}}$
Thus, $\mathrm{y}=\mathrm{m}_1 \mathrm{x}$ and $\mathrm{y}=\mathrm{m}_2 \mathrm{x}$ are two straight lines given by Eq. (i)
Real and Imaginary Lines
For equation (ii), if roots $m_1$ and $m_2$ are real, then the lines are also real, and if $m_1$ and $m_2$ are not real (imaginary), then the lines are also not real (imaginary). This depends on discriminant of equation (ii)
Discriminant $=4 \mathrm{~h}^2-4 \mathrm{ab}=4\left(\mathrm{~h}^2-\mathrm{ab}\right)$
1. The lines are real and distinct if $D>0: h^2-a b>0$
2. The lines are coincident if $D=0: h^2-a b=0$
3. The lines are imaginary if $D<0: h^2-a b<0$
Angle between pair of Straight Lines
General equation of pair of straight line is $\mathrm{ax}^2+2 \mathrm{hxy}+\mathrm{by}^2+2 \mathrm{gx}+2 \mathrm{fy}+\mathrm{c}=0$. Angle between the pair of the straight lines is
$
\theta=\tan ^{-1}\left\{\frac{2 \sqrt{\mathrm{~h}^2-\mathrm{ab}}}{|\mathrm{a}+\mathrm{b}|}\right\}
$
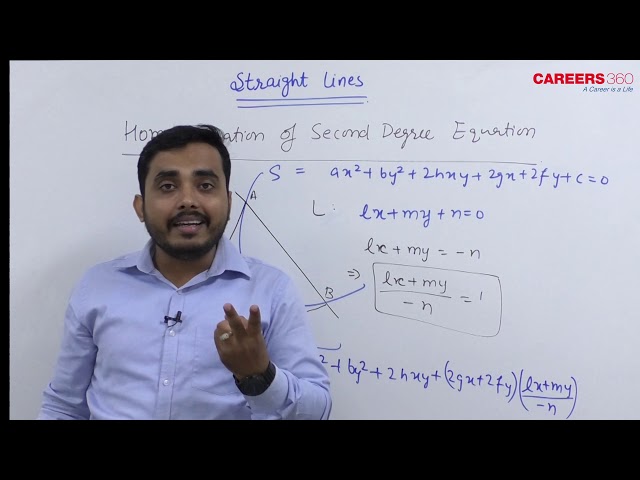
Homogenization of Second Degree Equation
Consider the general second degree equation
$
S \equiv a x^2+b y^2+2 h x y+2 g x+2 f y+c=0
$
This equation may represent a pair of the straight lines, circle, parabola, ellipse or hyperbola.

Now, let's a straight line : $\mathrm{L}=\mathrm{lx}+\mathrm{my}+\mathrm{n}=0$
(2) intersects the curve at two points $A$ and $B$.
The combined equation of pair of straight lines OA and OB must be homogenous and must contain only second-degree terms.
In order to make Eq (1) homogeneous using Eq (2), we can use (2) to writte
$
1=\frac{\mathrm{lx}+\mathrm{my}}{-\mathrm{n}}
$
now, equation of curve is
$
S \equiv\left(a x^2+2 h x y+b y^2\right)+(2 g x+2 f y) \cdot 1+c \cdot 1=0
$
put the value of 1 in above equation, we get
$
\left(a x^2+2 h x y+b y^2\right)+(2 g x+2 f y)\left(\frac{l x+m y}{-n}\right)+c\left(\frac{l x+m y}{-n}\right)^2=0
$
This will give a homogeneous equation of degree 2, and this represents the combined equation of OA and OB.
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"