Amity University-Noida B.Tech Admissions 2026
Among top 100 Universities Globally in the Times Higher Education (THE) Interdisciplinary Science Rankings 2026
15 Questions around this concept.
A block of mass 10 kg starts sliding on a surface with an initial velocity of $9.8 \mathrm{~ms}^{-1}$. The coefficient of friction between the surface and block is 0.5. The distance covered by the block before coming to rest is: $\left[\right.$ use $\left.\mathrm{g}=9.8 \mathrm{~ms}^{-2}\right]$
A bag is gently dropped on a conveyor belt moving at a speed of $2 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$. The coefficient of friction between the conveyor belt and bag is 0.4 . Initially, the bag slips on the belt before it stops due to friction. The distance travelled by the bag on the belt during slipping motion is: [Take $\mathrm{g}=10 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}^{-2}$ ]
A block of mass M slides down on a rough inclined plane with constant velocity. The angle made by the incline plane with horizontal is $\theta$. The magnitude of the contact force will be:
JEE Main 2026: Result OUT; Check Now | Final Answer Key Link
JEE Main 2026 Tools: College Predictor
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Link | Foreign Universities in India
As shown in the figure a block is given an initial velocity of $20 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$ in upward direction. What is the distance covered by the block to come to rest? $(g=10 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s})$

A small ball of mass m starts at point A with speed vo and moves along a frictionless track AB as shown. The track BC has coefficient of friction $\mu$. The ball comes to a stop at C after traveling a distance L which is :

Three masses $\mathrm{M}=100 \mathrm{~kg}, \mathrm{~m}_1=10 \mathrm{~kg}$ and $\mathrm{m}_2=20 \mathrm{~kg}$ are arranged in a system as shown in figure. All the surfaces are frictionless and strings are inextensible and weightless. The pulleys are also weightless and frictionless. A force F is applied on the system so that the mass $\mathrm{m}_2$ moves upward with an acceleration of $2 \mathrm{~ms}^{-2}$. The value of F is : $\left(\right.$ Take $\left.\mathrm{g}=10 \mathrm{~ms}^{-2}\right)$

A cubical box of side 'a' sitting on a rough table top is pushed horizontally with a gradually increasing force until the box moves. If the force is applied at a height from the tabletop which is greater than a critical height H, the box topples first. If it is applied at a height less than H, the box starts sliding first. Then the coefficient of friction between the box and the tabletop is
Among top 100 Universities Globally in the Times Higher Education (THE) Interdisciplinary Science Rankings 2026
Last Date to Apply: 26th March | Ranked #43 among Engineering colleges in India by NIRF | Highest Package 1.3 CR , 100% Placements
A cubical box of side a sitting on a rough table-top is pushed horizontally with a gradually increasing force until the box moves. If the force is applied at a height from the tabletop which is greater than a critical height H,the box topples first. If it is applied at a height less than H, the box starts sliding first . Then the coefficient of friction between the box and the tabletop is
A box when dropped from a certain height reaches the ground with a speed $\nu$. When it slides from rest from the same height down a rough inclined plane inclined at an angle $45^{\circ}$ to the horizontal, it reaches the ground with a speed $\nu / 3$. The coefficient of sliding friction between the box and the plane is (acceleration due to gravity is $10 \mathrm{~ms}^{-2}$ )
A force of 100 N is just sufficient to pull a block of mass $10 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~kg}$ on rough horizontal surface. What is angle friction? ( $\mathrm{g}=10 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}^2$ )
Case 1:- On the horizontal road
A block of mass m is moving initially with velocity u on a rough surface and due to friction, it comes to rest after covering a distance S.
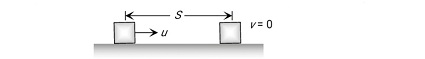

$
\begin{aligned}
& F=m a=\mu R \\
& m a=\mu m g \\
& a=\mu g \\
& V^2=u^2-2 a s \\
& S=\frac{u^2}{2 \mu g}=\frac{P^2}{2 \mu m^2 g} \\
& \mathrm{a}=\text { acceleration } \\
& \mu=\text { coefficient of friction } \\
& \mathrm{S}=\text { distance traveled } \\
& \mathrm{g}=\text { gravity } \\
& \mathrm{u}=\text { initial velocity } \\
& \mathrm{V}=\text { finally velocity } \\
& \mathrm{P}=\text { initial mometum=mu }
\end{aligned}
$
- Time taken to come to rest:
From equation $v=u-a t \Rightarrow 0=u-\mu g t \quad[$ As $v=0, a=\mu g]$
$
\therefore t=\frac{u}{\mu g}
$
- Force of friction acting on the body:
$
\begin{array}{ll}
F=m a & \\
F=m \frac{(v-u)}{t} & \\
F=\frac{m u}{t} & {[\text { As } v=0]} \\
F=\mu m g & {\left[\text { As } t=\frac{u}{\mu g}\right]}
\end{array}
$
Case 2:- On the inclined road :
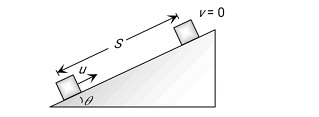

$\begin{aligned} & a=g[\sin \theta+\mu \cos \theta] \\ & V^2=u^2-2 a S \\ & 0=u^2-2 g[\sin \theta+\mu \cos \theta] S \\ & S=\frac{u^2}{2 g(\sin \theta+\mu \cos \theta)} \\ & \mathrm{S}=\text { distance traveled } \\ & \mu=\text { coefficient of friction } \\ & \mathrm{V}=\text { Final velocity } \\ & \mathrm{u}=\text { Initial velocity }\end{aligned}$
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"
