Skew Hermitian Matrix - Practice Questions & MCQ
Quick Facts
-
4 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
If matrix $A=\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0&w \\ 1& w^{2}& 1\\ 1& w^{2}& w \end{bmatrix}$ where $\omega$ is a cube root of unity. Then matrix $A-A^{\theta }$ is
Concepts Covered - 2
Skew-hermitian matrix
A square matrix $\mathrm{A}=\left[\mathrm{a}_{\mathrm{ij}}\right]_{\mathrm{n} \times \mathrm{n}}$ is said to be Skew-Hermitian matrix if $a_{i j}=-\overline{a_{i j}} \forall \mathrm{i}, \mathrm{j}_{\text {}}$
i.e. $\mathrm{A}^\theta=-\mathrm{A}, \quad\left[\right.$ where $\mathrm{A}^\theta$ is conjugate transpose of matrix A$]$
We know that when we take the transpose of a matrix, its diagonal elements remain the same, and while taking conjugate we just change sign from + ve to -ve $O R-v e$ to + ve in imaginary part of all elements, So to satisfy the condition $A$ ? $=-\mathrm{A}$, all diagonal element must be purely imaginary. As $A^?=-\mathrm{A}$ so
$\mathrm{a}_{\mathrm{ij}}=-\overline{\mathrm{a}_{\mathrm{ij}}} \forall \mathrm{i}, \mathrm{j}$
if we put $\mathrm{i}=\mathrm{j}$, we have
$
\mathrm{a}_{\mathrm{ii}}=-\overline{\mathrm{a}_{\mathrm{ii}}} \Rightarrow \mathrm{a}_{\mathrm{ii}}+\overline{\mathrm{a}_{\mathrm{ii}}}=0
$
$
\Rightarrow \mathrm{a}_{\mathrm{ii}}=0
$
Hence all diagonal element should be purely imaginary
E.g
Let, $\quad \mathrm{A}=\left[\begin{array}{ccc}-3 i & -3-4 i & -5+2 i \\ 3-4 i & 5 i & i \\ 5+2 i & i & 0\end{array}\right]$
Then,
$
\mathrm{A}^{\prime}=\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
-3 i & 3-4 i & 5+2 i \\
-3-4 i & 5 i & i \\
-5+2 i & i & 0
\end{array}\right]
$
Then,
$
\begin{aligned}
\mathrm{A}^{\prime} & =\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
-3 i & 3-4 i & 5+2 i \\
-3-4 i & 5 i & i \\
-5+2 i & i & 0
\end{array}\right] \\
\therefore \mathrm{A}^\theta & =\overline{\left(\mathrm{A}^{\prime}\right)}=\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
3 i & 3+4 i & 5-2 i \\
-3+4 i & -5 i & -i \\
-5-2 i & -i & 0
\end{array}\right] \\
& =-\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
-3 i & -3-4 i & -5+2 i \\
3-4 i & 5 i & i \\
5+2 i & i & 0
\end{array}\right]=-\mathrm{A}
\end{aligned}
$
here, A is Skew - Hermitian matrix as $\mathrm{A}^\theta=-\mathrm{A}$
Note:
1. for any square matrix $A$ with elements containing complex numbers, then $A-A$ ? is a skew hermitian matrix.
Proof: $\left(A-A^?\right)^?=A^?-\left(A^?\right)^?=A^?-A=-\left(A-A^?\right)$, hence skew-hermitian.
2. Every square matrix can be written as the sum of hermitian and skew-hermitian matrix i.e.
If $A$ is a square matrix, then we can write
$
A=\frac{1}{2}\left(A+A^\theta\right)+\frac{1}{2}\left(A-A^\theta\right)
$
Properties of hermitian and skew-hermitian matrices
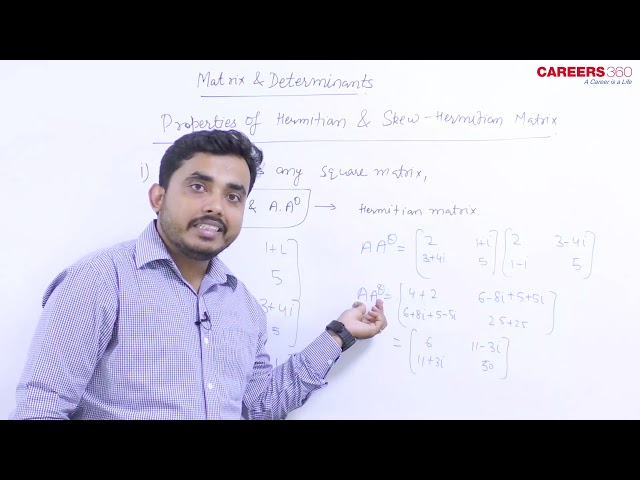
i) If A is a square matrix then AA𝛩 and A𝛩 A are hermitian matrix.
Proof: for hermitian matrix A𝛩 = A, so we check the condition on AA𝛩
(AA𝛩)𝛩 = (A𝛩)𝛩A𝛩 = AA𝛩 hence it is hermitian, and in the same way, A𝛩A will also be hermitian.
ii) If A is hermitian matrix then:
iA is a skew hermitian matrix, where i = √-1
Proof: we need to show (iA)𝛩 = -iA
(iA)𝛩= A𝛩i𝛩 = A𝛩 (-i) = -iA𝛩
Since A is hermitian so A𝛩 = A
Hence we have
-iA𝛩 = -iA. Proved.
iii) if A is a skew-hermitian matrix, then:
iA is a hermitian matrix, where i = √-1
Proof: we need to show (iA)𝛩 = iA
(iA)𝛩 = A𝛩i𝛩 = A𝛩(-i)
A𝛩(-i) = Ai = iA (since A is skew-hermitian, so A𝛩 = -A)
iv) if A and B are hermitian matrices of the same order, then
a. cA and dB are also hermitian matrices of the same order when c and d are scalar real constant.
Since A and B are of the same order, hence they are conformable for addition and by multiplying through a scalar we are just magnifying their values and nothing else, hence they will hold their property of hermitian matrices and cA + dB will be a hermitian matrix.
b. AB is also hermitian if AB = BA
Proof: (AB)𝛩 = B𝛩A𝛩 = BA = AB (Since A, B are hermitian so A𝛩 = A, B𝛩 =B)
c. AB + BA will also we hermitian
Proof: from part (b) AB and BA is hermitian and from part (c) AB + BA will also be hermitian.
d. AB - BA will be skew-hermitian
Proof: we need to show (AB-BA)* = -(AB-BA)
(AB-BA)* = (AB)* - (BA)* = B*A* - A*B* = BA - AB = -(AB - BA)
Using A𝛩 = A and B𝛩 = B, proved.
v) if A and B are skew hermitian matrix then cA +dB will be skew-hermitian
Proof are similar as above, just verify the basic condition, using the given condition of A and B.
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"