Calculation Of Necessary Force In Different Conditions On Rough Surface - Practice Questions & MCQ
Quick Facts
-
20 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
What is the minimum pushing force (in N) just to move the block?

Find the least force P which acting at an angle of $45^{\circ}$ with the horizontal, will slide a body weighing 6 kg along a rough horizontal surface. The coefficient of friction $\mu_s=\mu_k=\frac{1}{2}$. $\left(\right.$ use $\left.g=10 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}^2\right)$

A thin uniform, circular ring is rolling down an inclined plane of inclination 30° without slipping. Its linear acceleration along the inclined plane will be
JEE Main 2026: Result OUT; Check Now | Final Answer Key Link
JEE Main 2026 Tools: College Predictor
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Link | Foreign Universities in India
Concepts Covered - 4
-
Case 1:- Minimum pulling force P at an angle α from the horizontal


By resolving P in the horizontal and vertical direction, we get:


where F is the friction force.
For the condition of equilibrium,
$
\begin{aligned}
& F=P \cos \alpha \\
& R=W-P \sin \alpha
\end{aligned}
$
By substituting these values in $F=\mu R$, we get:
$
\begin{aligned}
& P \cos \alpha=\mu(W-P \sin \alpha) \\
& U s e=\mu=\tan \theta \\
& \Rightarrow P \cos \alpha=\frac{\sin \theta}{\cos \theta}(W-P \sin \alpha) \\
& P=\frac{W \sin \theta}{\cos (\alpha-\theta)}
\end{aligned}
$
where P is the pulling force,
R is a normal reaction
W is the weight
-
Case 2:- Minimum pushing force P at an angle α from the horizontal


By resolving P in the horizontal and vertical direction, we get:


For the condition of equilibrium,
$
\begin{aligned}
& F=P \cos \alpha \\
& R=W+P \sin \alpha
\end{aligned}
$
By substituting these values in $F=\mu R$, we get:
$
\begin{aligned}
& P \cos \alpha=\mu(W+P \sin \alpha) \\
& U s e=\mu=\tan \theta \\
& \Rightarrow P \cos \alpha=\frac{\sin \theta}{\cos \theta}(W+P \sin \alpha) \\
& P=\frac{W \sin \theta}{\cos (\alpha+\theta)}
\end{aligned}
$
-
Case 3:- Minimum pulling force P to move the body upwards on an inclined plane


By resolving P in the direction of the plane and perpendicular to the plane, we get:


For the condition of equilibrium
$
\begin{aligned}
& R+P \sin \alpha=W \cos \lambda \Rightarrow R=W \cos \lambda-P \sin \alpha \\
& F+W \sin \lambda=P \cos \alpha \Rightarrow F=P \cos \alpha-W \sin \lambda
\end{aligned}
$
By substituting these values in $F=\mu R$, we get:
$
P=\frac{W \sin (\theta+\lambda)}{\cos (\alpha-\theta)}
$
Where $\theta$ is the angle of friction such that, $\mu=\tan \theta$
-
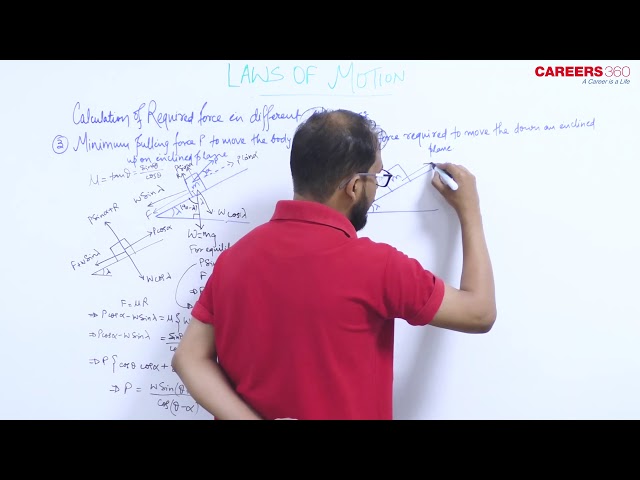
Case 4:- Minimum force to move a body in a downward direction along the surface of the inclined plane


By resolving P in the direction of the plane and perpendicular to the plane, we get:


For the condition of equilibrium,
$
\begin{aligned}
& R+P \sin \alpha=W \cos \lambda \Rightarrow R=W \cos \lambda-P \sin \alpha \\
& F=P \cos \alpha+W \sin \lambda
\end{aligned}
$
By substituting these values in $F=\mu R$, we get:
$
P=\frac{W \sin (\theta-\lambda)}{\cos (\alpha-\theta)}
$
Where $\theta$ is the angle of friction such that, $\mu=\tan \theta$
-
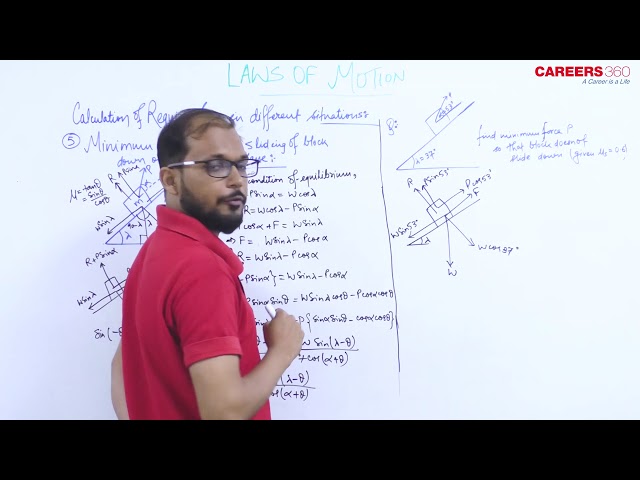
Case 5:- Minimum force to avoid sliding of a body down on an inclined plane

As the block has tendency to slip downward, friction force will act up the incline. For the minimum value of P, the friction force is limiting and the block is in equilibrium.
Free Body Diagram of the block-

For the condition of equilibrium-
$
\begin{aligned}
& \mathrm{R}+\mathrm{P} \sin \alpha=\mathrm{mg} \cos \lambda \\
& \Rightarrow \mathrm{R}=\mathrm{mg} \cos \lambda-\mathrm{P} \sin \alpha \\
& \text { Limiting friction }- \\
& \mathrm{f}_{\mathrm{l}}=\mu \mathrm{R} \\
& \Rightarrow f_l=\mu(m g \cos \lambda-P \sin \alpha) \ldots \ldots(1) \\
& f_l=m g \sin \lambda-P \cos \alpha \ldots(2) \\
& \text { From equation (1) and (2)- } \\
& m g \sin \lambda-P \cos \alpha=\mu(m g \cos \lambda-P \sin \alpha) \\
& \theta \rightarrow \operatorname{angle} \text { of friction } \\
& \mu=\tan \theta \\
& \mathrm{P}(\cos \alpha-\tan \theta \sin \alpha)=\mathrm{mg}(\sin \lambda-\tan \theta \cos \lambda) \\
& \Rightarrow P=\frac{m g \sin (\theta-\lambda)}{\cos (\theta+\alpha)}
\end{aligned}
$
-
Case 6:- Minimum Force of Motion along the horizontal surface and its direction

Let the force P be applied at an angle α with the horizontal.
Let the friction force on the block be F.
F.B.D of the block-

For vertical equilibrium,
$
\begin{aligned}
& \mathrm{R}+\mathrm{P} \sin \alpha=\mathrm{mg} \\
& \Rightarrow \therefore \mathrm{R}=\mathrm{mg}-\mathrm{Psin} \alpha
\end{aligned}
$
and for horizontal motion,
$
\mathrm{P} \cos \alpha \geq \mathrm{F} \Rightarrow \mathrm{P} \cos \alpha \geq \mu \mathrm{R}
$
Substituting the value of $R$, we get:-
$
\begin{aligned}
\mathrm{P} \cos \alpha & \geq \mu(\mathrm{mg}-\mathrm{P} \sin \alpha) \\
\Rightarrow \mathrm{P} & \geq \frac{\mu \mathrm{mg}}{\cos \alpha+\mu \sin \alpha}
\end{aligned}
$
For the force P to be minimum $(\cos \alpha+\mu \sin \alpha)$ must be maximum i.e.,
$
\begin{aligned}
& \frac{\mathrm{d}}{\mathrm{~d} \alpha}[\cos \alpha+\mu \sin \alpha]=0 \\
& \Rightarrow-\sin \alpha+\mu \cos \alpha=0 \\
& \therefore \tan \alpha=\mu \\
& \Rightarrow \alpha=\tan ^{-1}(\mu)=\text { angle of friction. }
\end{aligned}
$
i.e. For the minimum value of $P$, its angle from the horizontal should be equal to the angle of friction.
$\mathrm{As} \tan \alpha=\mu$, so from the figure,

$
\sin \alpha=\frac{\mu}{\sqrt{1+\mu^2}} \quad \operatorname{and} \quad \cos \alpha=\frac{1}{\sqrt{1+\mu^2}}
$
By substituting these values,
$
\begin{aligned}
\mathrm{P} & \geq \frac{\mu \mathrm{mg}}{\frac{1}{\sqrt{1+\mu^2}}+\frac{\mu^2}{\sqrt{1+\mu^2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \mathrm{P} \geq \frac{\mu \mathrm{mg}}{\sqrt{1+\mu^2}} \\
& \therefore \mathrm{P}_{\min }=\frac{\mu \mathrm{mg}}{\sqrt{1+\mu^2}}
\end{aligned}
$
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"