3D Geometry - Practice Questions & MCQ
Quick Facts
-
9 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
Any vector in a plane can be expressed as linear combination of 2 vectors in that plane where these 2 vectors are:
Any vector in space can be expressed as linear combination of 3 vectors in that space where these 3 vectors are:
Position vector of P is (where O is the origin):
JEE Main 2026: Result OUT; Check Now | Final Answer Key Link
JEE Main 2026 Tools: College Predictor
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Link | Foreign Universities in India
If sum of squares of distances of a point P from the three coordinate axes is 18 , then the distance of P from origin is
$
\text { The locus of the point which is equidistant from }(1,0,0) \text { and }(0,2,1) \text { is }
$
A point in the XZ plane is such that its X, Y, and Z coordinates are A.P with common difference 3 then the position vectors of the point will be
Concepts Covered - 1
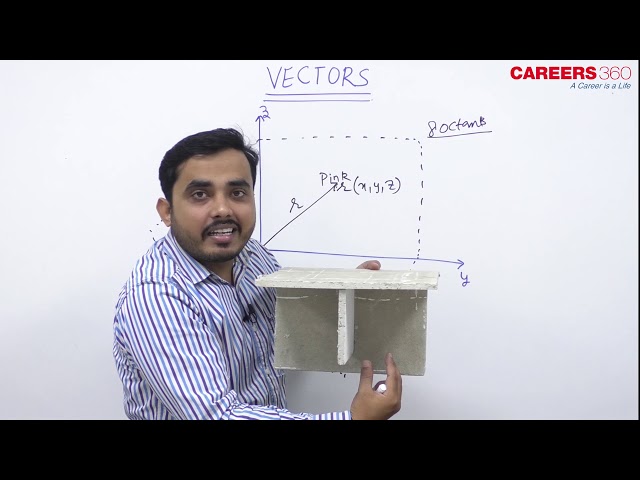
As we have learned, the two-dimensional rectangular coordinate system contains two perpendicular axes: the horizontal x-axis and the vertical y-axis. We can add a third dimension, the z-axis, which is perpendicular to both the x-axis and the y-axis. We call this system the three-dimensional rectangular coordinate system.

The system displayed follows the right-hand rule. If we take our right hand and align the fingers with the positive x-axis, then curl the fingers so they point in the direction of the positive y-axis, our thumb points in the direction of the positive z-axis. In this text, we always work with coordinate systems set up in accordance with the right-hand rule.
The three axes, X-axis, Y-axis and Z-axis are mutually perpendicular which defines three-dimensional (3D) coordinate system or space. Any point in this coordinate system has coordinates (x, y, z). Also, point in this system represents ordered triplets of set of cartesian product R x R x R Where, R is the set of real numbers.
If we take three axes, two at a time, then it will form three mutually perpendicular planes, XY-plane, YZ-plane and ZX-plane. This three plane divides space into eight regions called octants.

Coordinates of a Point in Space
Consider a point P(x, y, z) in three-dimensional system.

The x-coordinate of the point P is signed distance (OL) from the YZ-plane, i.e. a signed distance of P measured parallel to X-axis.
The y-coordinate of the point P is signed distance (ML) from the XZ-plane, i.e. a signed distance of P measured parallel to Y-axis.
The z-coordinate of the point P is signed distance (MP) from the XY-plane, i.e. a signed distance of P measured parallel to Z-axis.
The coordinates of the origin O are (0,0,0). The coordinates of any point on the x-axis will be as (x,0,0) and the coordinates of any point in the YZ-plane will be as (0, y, z).
The sign of the coordinates of a point determines the octant in which the point lies. The following table shows the signs of the coordinates in eight octants.

| Octant | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 6th | 7th |
8th |
| X | + | - | - | + | + | - | - | + |
| Y | + | + | - | - | + | + | - | - |
| Z | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | - |
Distance between Two Points:
Let P(x1 , y1 , z1 ) and Q ( x2 , y2 , z2 ) be two points in a three-dimensional system of rectangular axes OX, OY and OZ.

Since, PAQ is a right-angled triangle with ∠PAQ as a right angle,
Using the Pythagorean theorem
$
\mathrm{PQ}^2=\mathrm{PA}^2+\mathrm{AQ}^2
$
Also, triangle ANQ is a right angle triangle with $\angle A N Q$ aright angle.
$\therefore$
$
\mathrm{AQ}^2=\mathrm{AN}^2+\mathrm{QN}^2
$
from (i) and (ii)
$
\mathrm{PQ}^2=\mathrm{PA}^2+\mathrm{AN}^2+\mathrm{QN}^2
$
Now,
$
\mathrm{PA}=y_2-y_1, \mathrm{AN}=x_2-x_1 \text { and } \mathrm{NQ}=z_2-z_1
$
Hence,
$
\begin{aligned}
& \mathrm{PQ}^2=\left(x_2-x_1\right)^2+\left(y_2-y_1\right)^2+\left(z_2-z_1\right)^2 \\
\therefore & \mathrm{PQ}=\sqrt{\left(x_2-x_1\right)^2+\left(y_2-y_1\right)^2+\left(z_2-z_1\right)^2}
\end{aligned}
$
This gives us the distance between two points P(x1 , y1 , z1 ) and Q ( x2 , y2 , z2 )
Distance of a point from the Axes and Origin
Distance of a point from $x$-axis is $\sqrt{\mathrm{y}^2+\mathrm{z}^2}$.
Distance of a point from $y-a x i s$ is $\sqrt{\mathrm{x}^2+\mathrm{z}^2}$.
Distance of a point from $z-a x i s$ is $\sqrt{\mathrm{y}^2+\mathrm{x}^2}$.
Distance from Origin
If $x_2=y_2=z_2=0$, i.e., point $Q$ is origin $O$, then $\mathrm{OP}=\sqrt{x_1^2+y_1^2+z_1^2}$
which gives the distance between the origin O and any point P(x1, y1, z1)
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"