Sign of Trigonometric Functions - Practice Questions & MCQ
Quick Facts
-
7 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
$\sin \left ( \frac{-2\pi}{3} \right )$ equals
Concepts Covered - 1
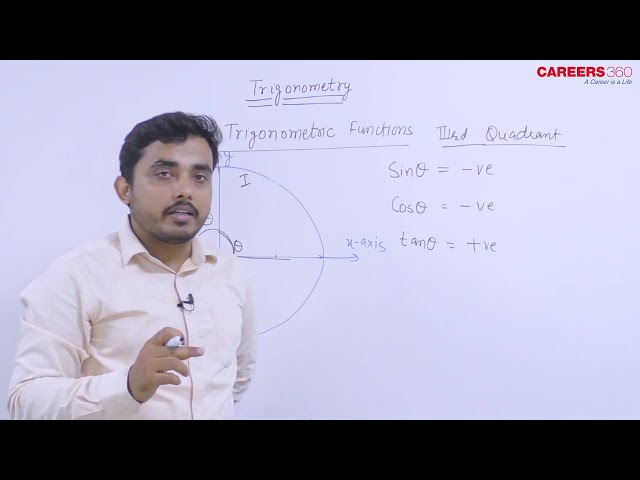
Sign of Trigonometric Functions
The sign of trigonometric ratios of an angle depends on the quadrant in which the terminal side of the angle lies. We always take OP = r as positive. Thus, the sign of trigonometric functions depends on the sign of x and y.

An angle is said to be in a quadrant in which its terminal ray lies (here terminal ray is OP).
In the first quadrant x and y are positive so sin θ, cos θ, tan θ, sec θ, csc θ, and cot θ are all positive.
In the second quadrant, x is negative and y is positive, so only sin θ and cosec θ are positive.
In the third quadrant, x is negative and y is negative, so only tan θ and cot θ are positive.
In the fourth quadrant, x is positive and y is negative, so only cos θ and sec θ are positive.
To help us remember which of the six trigonometric functions are positive in each quadrant, we can use the mnemonic phrase “After School to College". Each of the four words in the phrase corresponds to one of the four quadrants, starting with quadrant I and rotating counterclockwise.

Depending on the sign of x and y, the various trigonometric ratios will have different signs given.
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"