Amity University-Noida B.Tech Admissions 2026
Among top 100 Universities Globally in the Times Higher Education (THE) Interdisciplinary Science Rankings 2026
Refraction Through A Prism 1, Dispersion Of Light 1 is considered one of the most asked concept.
68 Questions around this concept.
A ray of light is incident at an angle of $60^{\circ}$ on one face of a prism of angle $30^{\circ}$. The emergent ray of light makes an angle of $30^{\circ}$ with the incident ray. The angle made by the emergent ray with the second face of the prism will be:
A ray of light AO in a vacuum is incident on a glass slab at angle $60^{\circ}$ and refracted at angle $30^{\circ}$ along OB as shown in the figure. The optical path length of light ray from $A$ to $B$ is:
A liquid is placed in a hollow prism at an angle of 60o. If angle of the minimum deviation is 30o, what is the refractive index of the liquid?
JEE Main 2026: Result OUT; Check Now | Final Answer Key Link
JEE Main 2026 Tools: College Predictor
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Link | Foreign Universities in India
The expected graphical representation of the variation of the angle of deviation '$\delta$' with the angle of incidence 'i' in a prism is :
A prism can produce a minimum deviation d in a light beam. If three such prisms are combined, the minimum deviation that can be produced in this beam is:
A ray of light passes through an equilateral prism such that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of emergence and the latter is equal to 3/4th the angle of the prism. The angle of deviation is:
Direction: In the following question, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: Refractive index of material depends on angle of minimum deviation $\delta m$ and angle of prism A.
Reason : Refractive index of material is given by $\mu=\frac{\sin \left(\frac{A+\delta m}{2}\right)}{\sin (A / 4)}$
Among top 100 Universities Globally in the Times Higher Education (THE) Interdisciplinary Science Rankings 2026
Last Date to Apply: 28th Feb | Ranked #43 among Engineering colleges in India by NIRF | Highest Package 1.3 CR , 100% Placements
A thin prism of glass is placed in air and water successively. If μg = 3/2 and μw = 4/3, then the ratio of deviations produced by the prism for a small angle of incidence when placed in air and water is :
It was found that the refractive index of the material of a certain prism varied as $1.5+0.004 / \lambda^2$, where $\lambda$ is the wavelength of light used to measure the refractive index. The same material was then used to construct a thin prism with an apex angle of $10^{\circ}$. Angles of minimum deviation ( $\delta \mathrm{m}$ ) of the prism were recorded for the sources with wavelengths $\lambda_1$ and $\lambda_2$ respectively. Then
Select the correct statement about the rainbow:
A prism is a transparent medium whose refracting surfaces are not parallel but are inclined to each other at an angle A which is also known as angle of the prism.

The angle of deviation $(\delta) {\text {-It is the angle between the emergent and the incident ray. }}$
For the above figure $\delta=\left(i-r_1\right)+\left(e-r_2\right)$ or $\delta=i+e-\left(r_1+r_2\right)$ and using $U \operatorname{sing} \quad A=r_1+r_2$ we get $\delta=i+e-A$
Note-From the above formula, we can say that if we interchange i and e then also we will get the same value of $\delta$.
The plot of $\delta$ vs $i$

As shown in the above figure The graph is a parabola.
If we vary i between $0^0$ to $90^0$
then for $0<i<e_{\text {the }}$ value of $\delta$ decreases
and for $e<i<90$ the value of $\delta$ increases
And when $i=e$ then $\delta=\delta_{\text {min }}$
and when $i=90^{\circ}$ or $e=90^{\circ} \quad$ then $\delta=\delta_{\max }$
- Grazing Incidence-When $\mathrm{i}=90^{\circ}$, the incident ray grazes along the surface of the prism. This is known as grazing incidence.
- Grazing Emergence- When $\mathrm{e}=90^{\circ}$, the emergent ray grazes along the prism surface. This is known as grazing emergence.
This happens when the light ray strikes the second face of the prism at the critical angle for glass - air.
I.e when $r_2=\theta_c$ then $e=90^{\circ}$
I.e For the prism of refractive index $\mu$ places in the air.
then $i=\sin ^{-1}\left[\sqrt{\mu^2-1} \sin A-\cos A\right]$ then $\mathrm{e}=90^{\circ}$
Refractive index of prism $(\mu)$ in case of minimum deviation condition-
As we learned The angle of deviation $(\delta)$ for the prism is given as $\delta=i+e-A$ and from The plot of $\delta$ vs $i$ we get $i=e$ then $\delta=\delta_{\min }$
$
\begin{aligned}
& \text { i.e } \delta_{\min }=i+e-A=i+i-A=2 i-A \\
\Rightarrow & i=\frac{A+\delta_{\min }}{2}
\end{aligned}
$

For the prism of refractive index $\mu_{\text {places in the air. }}$
For the first surface, we can write $1 * \sin i=\mu \sin r_1$
similarly For the second surface, we can write $\mu \sin r_2=1 * \operatorname{sine}$
using i=e we get $r_1=r_2$
$
\begin{aligned}
A & =r_1+r_2=2 r_1 \\
\rightarrow r_1 & =\frac{A}{2}
\end{aligned}
$
So $1 * \sin i=\mu \sin r_1$ will give us
$
\begin{aligned}
& \Rightarrow 1 * \sin \left(\frac{A+\delta_{\min }}{2}\right)=\mu \sin \left(\frac{A}{2}\right) \\
\Rightarrow \mu & =\frac{\sin \left(\frac{A+\delta_{\min }}{2}\right)}{\sin \left(\frac{A}{2}\right)}
\end{aligned}
$
- For thin films (i.e $A$ and $\delta_{\min }$ are small)
Then $\sin \left(\frac{A+\delta_{\text {min }}}{2}\right)=\frac{A+\delta_{\text {min }}}{2}$
$
\text { and } \sin \left(\frac{A}{2}\right)=\frac{A}{2}
$
So we get
$
\begin{gathered}
\mu=\frac{A+\delta_{\min }}{A} \\
\Rightarrow \delta_{\min }=A(\mu-1)
\end{gathered}
$
- condition of no emergence-
i.e A ray of light incidence on a prism of angle A and refractive index $\mu$ will not emerge out of a prism This will happen when $A>2 \theta_c$
where $\theta_c=$ critical angle
Dispersion of light -The splitting of white light into its constituent colors or wavelengths is called dispersion of light.
or
angular splitting of a ray of white light into a number of components and spreading in different directions is called diversion of light.
This phenomenon arises due to the fact that the refractive index varies with wavelength.
When white light is incident on the prism it will split itself into its constituent colors as shown in the below figure.
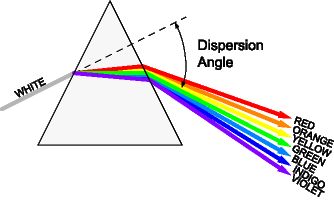
The deviation is given as $\delta=(\mu-1) A$
Since $\mu_{\text {violet }}>\mu_{\text {red }}$
So $\delta_{\text {violet }}>\delta_{\text {red }}$
- Angular dispersion $(\theta)$-Angular separation between extreme colors i.e $\boldsymbol{\theta}=\boldsymbol{\delta}_V-\boldsymbol{\delta}_R=\left(\boldsymbol{\mu}_V-\boldsymbol{\mu}_R\right) \boldsymbol{A}$.
It depends upon $\mu$ and A .
- Dispersive power $(\omega)$ - Ratio of angular dispersion to mean deviation.
$
\omega=\frac{\delta_v-\delta_r}{\delta}
$
where where $\delta$ is deviation of mean ray (especially yellow)
$u \operatorname{sing} \quad \delta_v=\left(\mu_v-1\right) A, \delta_r=\left(\mu_r-1\right) A$
we get $\omega=\frac{\mu_v-\mu_r}{\mu_y-1} \quad$ where $\quad \mu_y=\frac{\mu_v-\mu_r}{2}$
where
$\mu_v=$ Refractive index of violet
$\mu_r=$ Refractive index of red
$\mu_y=$ Refractive index of yellow
Condition for deviation without dispersion-
This means an achromatic combination of two prisms in which net(or) resultant dispersion is 0, but and deviation is produced as shown in the below figure.
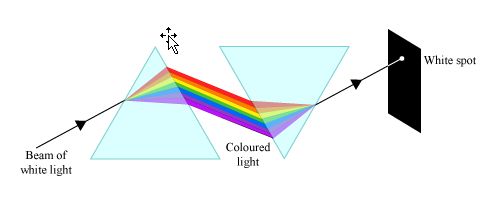
For the two prisms,
$
\begin{gathered}
\theta_{\text {net }}=0 \Rightarrow \theta_1+\theta_2=0 \\
\left(\mu_v-\mu_r\right) A+\left(\mu_v^{\prime}-\mu_r^{\prime}\right) A^{\prime}=0 \\
\Rightarrow \quad A^{\prime}=\frac{\left(\mu_v-\mu_r\right) A}{\mu_v^{\prime}-\mu_r^{\prime}}
\end{gathered}
$
where
$\mu_v=$ Refractive index of violet ( prism 1)
$\mu_r=$ Refractive index of red ( prism 1)
$\mu_v^{\prime}=$ Refractive index of violet ( prism 2)
$\mu_r^{\prime}=$ Refractive index of red ( prism 2)
Similarly
For the two prisms,
$
\begin{aligned}
& \theta_{\text {net }}=0 \Rightarrow \theta_1+\theta_2=0 \\
& \omega \delta+\omega^{\prime} \delta^{\prime}=0 \\
\Rightarrow & \delta^{\prime}=-\delta \frac{\omega}{\omega^{\prime}} \\
\Rightarrow & \delta_{\text {net }}=\delta+\delta^{\prime}=\delta\left[1-\frac{\omega}{\omega^{\prime}}\right]
\end{aligned}
$
where $\omega$ and $\omega^{\prime}$ are the dispersive powers of the two prisms and their corresponding mean deviations are $\delta$ and $\delta^{\prime}$.
Condition for Dispersion without deviation-
A combination of two prisms in which deviation produced for the mean ray by the first prism is equal and opposite to that produced
by the second prism will give a dispersion of light without deviation.
This combination of two prisms is also called a direct vision prism.
i.e $\delta_{\text {net }}=0$ while $\theta_{\text {net }} \neq 0$

As shown in the above figure as emergent rays from the second prism is parallel to the incident white ray of prism 1.
this will give $\delta_{n e t}=0$.
For zero deviation,
$
\begin{array}{r}
\text { i.e } \delta_{\text {net }}=0\left(\text { i.e } \delta+\delta^{\prime}=0\right) \\
\Rightarrow \quad\left(\mu_y-1\right) A+\left(\mu_y^{\prime}-1\right) A^{\prime}=0 \\
\Rightarrow \quad A^{\prime}=\frac{\left(\mu_y-1\right) A}{\left(\mu_y^{\prime}-1\right)}
\end{array}
$
and the Angular dispersion is given as
$
\theta_{\mathrm{net}}=\theta_1+\theta_2=\left(\omega \delta+\omega^{\prime} \delta^{\prime}\right)=\left(\omega \delta-\omega^{\prime} \delta\right)=\theta\left(1-\frac{\omega^{\prime}}{\omega}\right)
$
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"
