Real Depth And Apparent Depth - Practice Questions & MCQ
Quick Facts
-
Real depth and Apparent depth is considered one the most difficult concept.
-
26 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
At the bottom of a tank having liquid with refractive index, 'm' is a plane mirror. A small object 'M' is situated at a height 'd' above the mirror. Object ' M ' and its image in the mirror are visible to an observer who is 'O' vertically above M outside the liquid. The object 'M' and its image will appear to be separated by how much distance?
Concepts Covered - 1
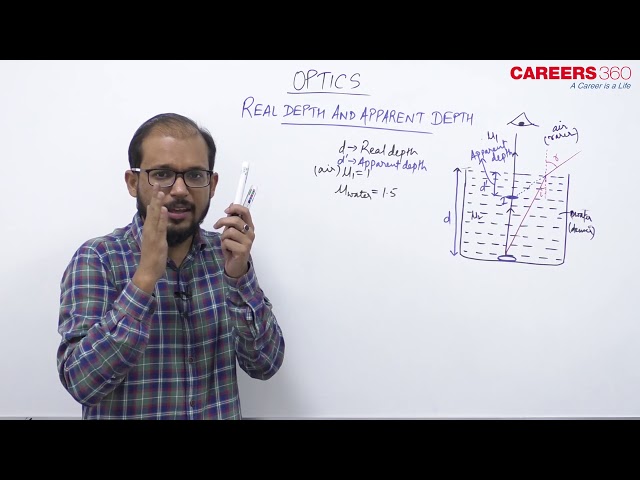
Real depth and Apparent depth
Case 1. When object is in denser medium and observer is in rarer medium.
If object and observer are situated in different medium then due to refraction, object appears to be displaced from it's real position.

Here O is the real position of the object and O' is the apparent position of the object as seen by the observer. 'h' is the real depth of the object from the surface of the water and h' is the apparent depth of the object. is the density of the medium where the object is placed.
is the density of the rarer medium.
$
\frac{\mu_2}{\mu_1}=\frac{\text { Real depth }}{\text { Apparent depth }}=\frac{h}{h^{\prime}}
$
Therefore Real depth > Apparent depth.
Apparent shift:
$
d=h-h^{\prime}=\left(1-\frac{\mu_1}{\mu_2}\right) h
$
Case 2. Object is in rarer medium and observer is in denser medium.

$
\frac{\mu_2}{\mu_1}=\frac{\text { Apparent depth }}{\text { Real depth }}=\frac{h^{\prime}}{h}
$
Therefore apparent depth > real depth.
Apparent shift:
$
d=\left(\frac{\mu_1}{\mu_2}-1\right) h
$
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"