Radical Axis - Practice Questions & MCQ
Quick Facts
-
18 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
If the circumference of the circle is bisected by the circle
, then
The equation of the radical axis of the two circles and
is given by
The equation of a circle which passes through and whose radical axis in relation to the circle
is
, is
JEE Main 2026: Result OUT; Check Now | Final Answer Key Link
JEE Main 2026 Tools: College Predictor
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Link | Foreign Universities in India
The gradient of the radical axis of the circles $\mathrm{x}^2+\mathrm{y}^2-3 \mathrm{x}-4 \mathrm{y}+5=0$ and $3 \mathrm{x}^2+3 \mathrm{y}^2-7 \mathrm{x}+8 \mathrm{y}+11=0$ is:
The equation of the circle, which passes through the point $(2 \mathrm{a}, 0)$ and whose radical axis is $\mathrm{x}=\frac{\mathrm{a}}{2}$ with respect to the circle $\mathrm{x}^2+\mathrm{y}^2=\mathrm{a}^2$, will be:
The radical axis of the two distinct circles x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 and 2x2 + 2y2 + 4x + y + 2c = 0 touches the circle x2 + y2 − 4x − 4y + 4 = 0. Then the centre of the circle x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 can be
Concepts Covered - 1
Radical Axis
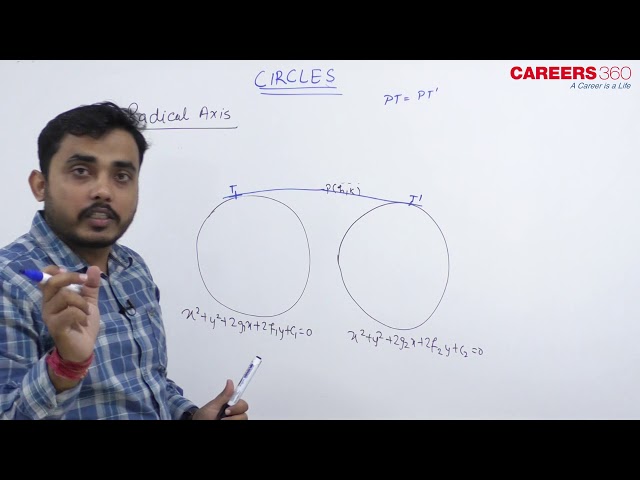
The radical axis of two circles is the locus of a point which moves in a plane in such a way that the lengths of the tangents drawn from it to the two circles are the same.
Consider the two circles:
$
\begin{aligned}
& S_1: x^2+y^2+2 g_1 x+2 f_1 y+c_1=0 \\
& S_2: x^2+y^2+2 g_2 x+2 f_2 y+c_2=0
\end{aligned}
$
Let point $\mathrm{P}\left(\mathrm{x}_1, \mathrm{y}_1\right)$ such that
$
|\mathrm{PA}|=|\mathrm{PB}|
$


The length of the tangent from a point $\mathrm{P}\left(\mathrm{x}_1, \mathrm{y}_1\right)$ to circle S is $\sqrt{S_1}$
$
\Rightarrow \sqrt{x_1^2+y_1^2+2 g_1 x_1+2 f_1 y_1+c_1}=\sqrt{x_1^2+y_1^2+2 g_2 x_1+2 f_2 y_1+c_2}
$
Square both sides, and we get
$
\begin{aligned}
& \Rightarrow \mathrm{x}_1^2+\mathrm{y}_1^2+2 \mathrm{~g}_1 \mathrm{x}_1+2 \mathrm{f}_1 \mathrm{y}_1+\mathrm{c}_1=\mathrm{x}_1^2+\mathrm{y}_1^2+2 \mathrm{~g}_2 \mathrm{x}_1+2 \mathrm{f}_2 \mathrm{y}_1+\mathrm{c}_2 \\
& \Rightarrow 2 \mathrm{x}_1\left(\mathrm{~g}_1-\mathrm{g}_2\right)+2 \mathrm{y}_1\left(\mathrm{f}_1-\mathrm{f}_2\right)+\mathrm{c}_1-\mathrm{c}_2=0
\end{aligned}
$
This is the required equation of the radical axis.
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"