Huygens Principle - Practice Questions & MCQ
Quick Facts
-
21 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
When a wave undergoes reflection at an interface from a rarer to a denser medium, adhoc change in its phase is:
Which of the following is true regarding the angle of incidence and angle of refraction in refraction?
A light wave is incident from air to a medium with a refractive index of 1.5. If the angle of incidence is 45 degrees, what is the angle of refraction?
JEE Main 2026: Result OUT; Check Now | Final Answer Key Link
JEE Main 2026 Tools: College Predictor
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Link | Foreign Universities in India
Concepts Covered - 3
According to the Huygens principle , Every point on the given wavefront acts as a source of a new disturbance called secondary wavelets. And a common tangent to these secondary wavelets in the forward direction at any instant gives the new wavefront at that instant as shown in the below figure. This is called secondary wavefront.

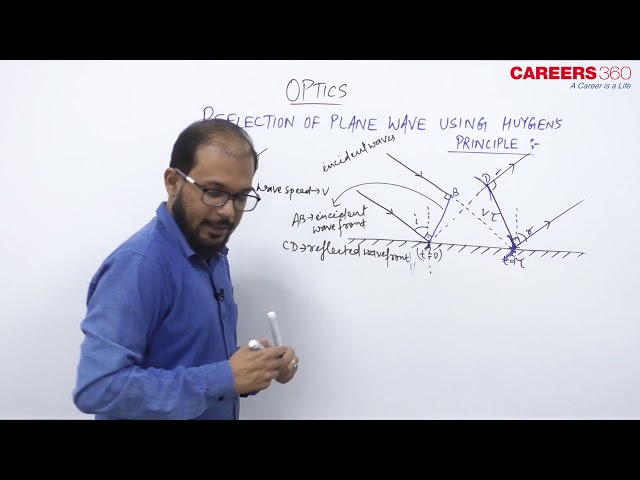
The Lightwave will follow the Laws of Reflection. Let's understand this with the help of the Huygens principle.
Consider a plane wavefronts travels towards a plane reflecting surface as shown in the figure.

Let $A B$ and $C D$ as the incident and reflected wavefronts respectively.
The angle of incidence $i$ and angle of reflection $r$ are the angles made by incidence and reflected ray respectively with the normal and these are also the angles made by the wavefronts $A B$ and $C D$ respectively with the reflecting surface.
Let at $\mathrm{t}=0$ wave is at A and at $t=\tau$ wave is at C .
if $\mathrm{v}_1$ is the velocity of the wave $B C=A D=v_1 \tau$
And as $\triangle A B C \cong \triangle A D C$ So we get $i=r$.
This verifies the first law of reflection which states that the angle of incidence i and angle of reflection r are always equal.
Similarly from the figure, we can say that the incident wavefront, the reflected wavefront and normal lie in the same plane.
This again verifies the second law of reflection.
Therefore, the two laws of Reflection are verified using Huygens's Principle.
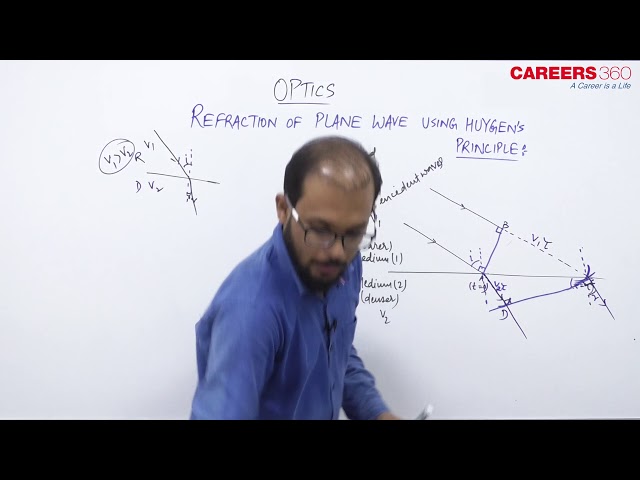
The Lightwave will follow the Laws of Refraction. Let's understand this with the help of the Huygens principle.

Consider a plane wavefronts travels towards a plane AC as shown in the above figure.
Let AB and CD as the incident and refracted wavefronts respectively.
The angle of incidence i and angle of refraction r are the angles made by incidence and refracted ray respectively with the normal and these are also the angles made by the wavefronts AB and CD respectively with the surface AC.
Let at $\mathrm{t}=0$ wave is at A and at $t=\tau$ wave is at C .
if $\mathrm{v}_1$ is the velocity of the wave in medium 1 then $B C=v_1 \tau$
similarly $\mathrm{v}_2$ is the velocity of the wave in the medium 2 then $A D=v_2 \tau$
For $\triangle A B C \rightarrow \sin (i)=\frac{B C}{A C}=\frac{v_1 \tau}{A C}$
similarly
$
\text { For } \triangle A C D \rightarrow \sin (r)=\frac{A D}{A C}=\frac{v_2 \tau}{A C}
$
So we get $\frac{\sin (i)}{\sin (r)}=\frac{v_1 \tau}{v_2 \tau}=\frac{v_1}{v_2}$
And we know $\mu \quad \alpha \quad v$
So we get
$
\frac{\sin (i)}{\sin (r)}=\frac{v_1}{v_2}=\frac{\mu_2}{\mu_1}=\mu_{21}=\text { constant }
$
This verifies the first law of refraction.
Similarly from the figure, we can say that the incident wavefront, the refracted wavefront and normal lie in the same plane.
This again verifies the second law of Refraction.
Therefore, the two laws of Refraction are verified using Huygens's Principle.
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"