Degree Of Freedom - Practice Questions & MCQ
Quick Facts
-
22 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
Consider a gas of triatomic molecules. The molecules are assumed to be triangular and made of massless rigid rods whose vertices are occupied by atoms. The internal energy of a mole of the gas at temperature T is
A gas mixture contains 3 moles of oxygen and x mole of monoatomic gas at temperature T Considering only translational and rotational but not vibrational modes, the total energy of the system is 15 RT then the value of x is.
If N = no. of particle
R = NO. of relation
and f = degree of freedom
then f can be given as
JEE Main 2026: Result OUT; Check Now | Final Answer Key Link
JEE Main 2026 Tools: College Predictor
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Link | Foreign Universities in India
Direction: In the following question, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R) . Mark the correct choice as :
Assertion : The value of $C_v / C_p$ is more for helium gas than for hydrogen gas
Reason : Atomic mass of helium is more than that of hydrogen
Energy of 10 non rigid diatomic molecules at temperature T is:
Direction: In the following question, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as :
Assertion : The ratio $\frac{C_p}{C_u}$ for monoatomic gas is more than for a diatomic gas
Reason: monoatomic gas have, an ore degree of freedom than those of a diatomic gas
Concepts Covered - 1
Degree of freedom-
The degree of freedom of systems is defined as the possible independent motions, systems can have.
Or
The degree of freedom of systems is defined as the number of independent coordinates required to describe the system completely.
The independent motions can be translational, rotational or vibrational or any combination of these.
So the degree of freedom is of three types :
(i) Translational degree of freedom
(ii) Rotational degree of freedom
(iii) Vibrational degree of freedom
The degree of freedom is denoted by .
And it is given by
$
f=3 N-R
$
Where
$N=$ no. of particle
$R=$ no. of relation
- Value of degree of freedom for
1.Monoatomic gas-
A monoatomic gas can only have a translational degree of freedom.
l.e $f=3$
Example- $\mathrm{He}, \mathrm{Ne}, \mathrm{Ar}$
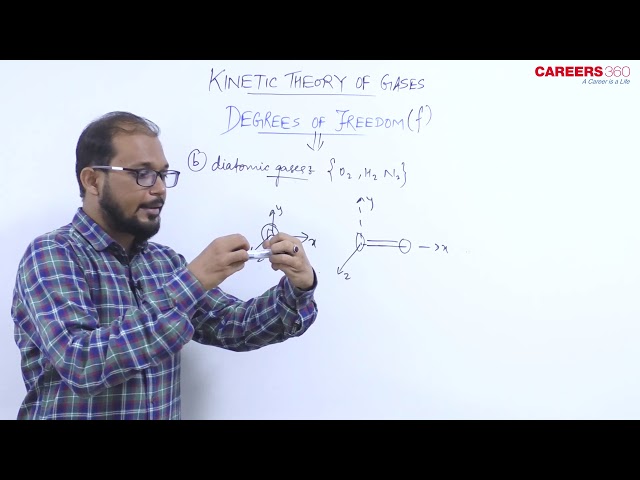
2. Diatomic gas
A diatomic gas can have three translational degrees of freedom and two rotational degrees of freedom.
I.e $f=5$
Example- $\mathrm{H}_2, \mathrm{O}_2, \mathrm{~N}_2$
3. Triatomic gas
A triatomic gas can have three translational degrees of freedom and three rotational degrees of freedom.
I.e $f=6$
Example- $\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}$
- Note-
The above degrees of freedom are shown at room temperature. Further at high temperature, in the case of diatomic or polyatomic molecules,
the atoms within the molecule may also vibrate with respect to each other. In such cases, the molecule will have 2 additional degrees of freedom, due to vibrational motion. I.e One for the potential energy and one for the kinetic energy of vibration.
So A diatomic molecule that is free to vibrate (in addition to translation and rotation) will have 7 degrees of freedom.
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"