Concave And Convex Lenses - Image Formation - Practice Questions & MCQ
Quick Facts
-
29 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
The focal length of the lens as shown in the figure is:

The refractive index of the material of a concave lens is $\mu$. It is immersed in a medium of refractive index $\mu_{1.}$ A parallel beam of light is incident on the lens. The path of the emergent rays when $\mu_1>\mu$ is :
Given below are two statements:
Statement (I): When an object is placed at the centre of curvature of a concave lens, image is formed at the centre of curvature of the lens on the other side.
Statement (II): Concave lens always forms a virtual and erect image.In the light of the above statements,
choose the correct answer from the options given below:
JEE Main 2026: Result OUT; Check Now | Final Answer Key Link
JEE Main 2026 Tools: College Predictor
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Link | Foreign Universities in India
If the behaviour of light rays through a convex lens is as shown in the adjoining figure, then;
If the image formed by a thin convex lens of power P has magnification m then image distance v is:
A convex lens is used to form an image of an object on a screen. If the upper half of the lens is blackened so that it becomes opaque, then
Concepts Covered - 2
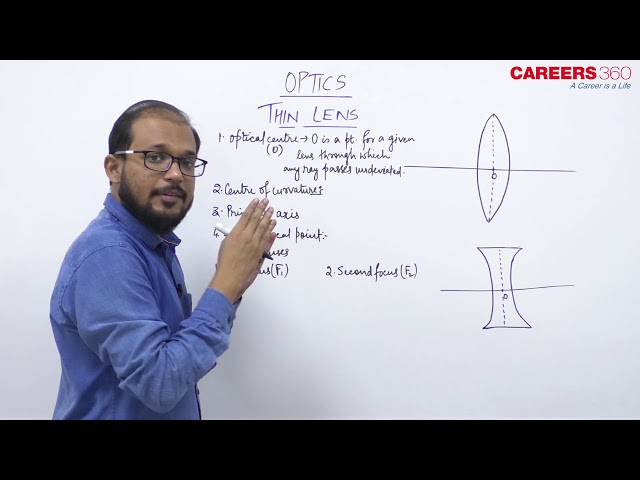
Thin lens-
A lens is a transparent medium bounded by two surfaces which refract the light, such that at least one surface is curved. The curved surface can be cylindrical, spherical etc.
A thin lens is called convex if it is thicker in the middle as compared to the ends and it is called concave if it is thicker at the ends as compared to the middle. The figure shows the convex and concave lens -

There are few types of concave and convex lens as shown below -

From all the above shapes we can see that there are two surfaces (may be spherical or plane), so there are two centres of curvature C1 and C2 and correspondingly two radii of curvature R1 and R2. In this case, the principal axis is the line joining C1 and C2 of the lens and the centre of the thin lens which is on the principal axis, is called the optical centre.
Now as there are two surfaces in the lens so there are two principal focuses for the lens, which are:-
First principal focus(F1): An object point for which an image is formed at infinity.

Second principal focus(F2): An image point for an object at infinity.

Note -
1. In this chapter we are mainly concerned with the second principal focus (F2). So, whenever or wherever we use the term focus, it means the second principal focus.
2. A ray passing through the optical centre proceeds undeviated through the lens.
SIgn convention in the lens - All the distances along the direction of the incident light ray are positive if we measure the distances from the pole of the lens. Also, all the distances above the principal axis are taken as positive and below the principal axis are taken as negative. All these conventions can be seen in the figure given below -

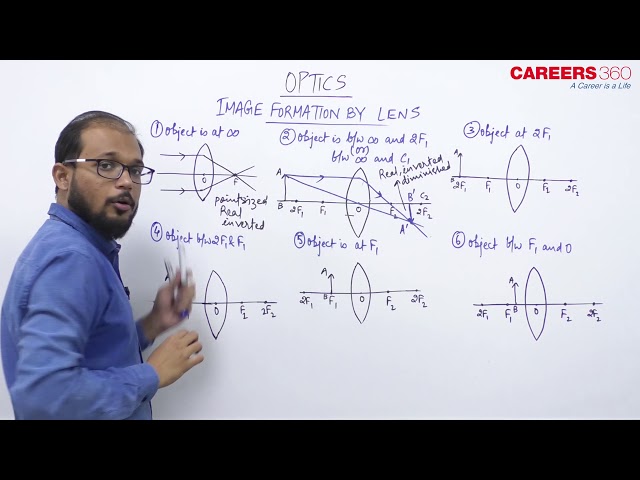
Image formation by lens-
In this concept we will discuss how and where the image will form with different position of object in concave and convex lens. Let us discuss both the lens one by one -
Convex lens -
The figure given below is showing the position of image formation for different position of the object -

So, from this image we can conclude the floolwing table -
For convex lens -
|
Object location |
Image location | Image nature |
Image size |
| Infinity | At F | Real and Inverted | Diminished |
| Beyond 2F | Between 2F and F | Real and Inverted | Diminished |
| Between 2F and F | Beyond 2F | Real and Inverted | Enlarged |
| At F | At infinity | Real and Inverted | Enlarged |
| At 2F | At 2F | Real and Inverted | Same size |
| Between F and 0 | On the same side as object | Virtual and Erect | Enlarged |
For concave lens -
| Object location | Image location | Image nature | Image size |
| Infinity | At F | Virtual and Erect | Highly Diminished |
| Beyond infinity and 0 | Between F and Optical centre | Virtual and Erect | Diminished |
Note - In the table O is the optical center of the lens.
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"