Rotational Motion Of Rigid Body - Practice Questions & MCQ
Quick Facts
-
8 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
In the rotational motion of a rigid body, all particle move with
All the particles of a rigid body moves in a circular path then the axis rotation
Concepts Covered - 1
-
Rigid body-
It is defined as a system of particles in which the distance between each pair of particle remains constant.
This means the shape & size do not change during the motion.
-
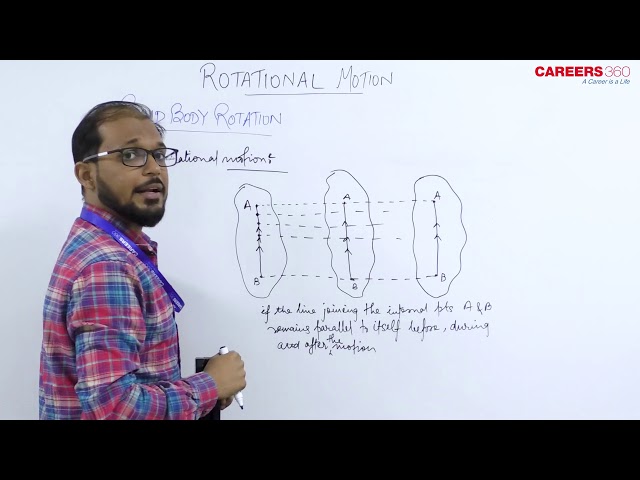
Translation motion-
If a body is moving such that a line drawn between any two of its internal points remain parallel to itself.
All the particles of the body move along parallel paths.
All the particles of the body follows 1 D motion.
Example- Motion of a body along a straight line.
-
Rotational motion-
A rigid body is said to be in pure rotation if every particle of the body moves in a circle and centre of all the circles lie on a straight line called the axis of rotation.
The line joining any two internal points does not remain parallel.
Example-motion of wheels, gears, motors.
-
Some important terms-
-
System-
A system is a collection of any number of particles interacting with one another and are under observation for analysing the situation.
-
Internal forces-
Internal forces are all the forces exerted by various particles of the system on one another . Internal forces between two particles are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction.
-
External forces-
External forces are the forces that we have to apply on the object/system from outside to move or stop an object/system.
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"