Mutual Inductance - Practice Questions & MCQ
Quick Facts
-
Mutual Inductance, Mutual Inductance for two coaxial long solenoids, Mutual Inductance for a pair of concentric coils is considered one of the most asked concept.
-
53 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
The unit of mutual inductance is
Concepts Covered - 3
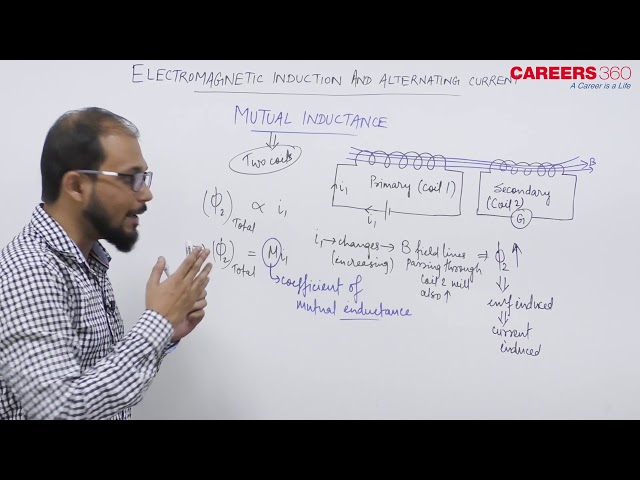
Whenever the current passing through a coil or circuit changes, the magnetic flux linked with a neighboring coil or circuit will also change. Hence an emf will be induced in the neighboring coil or circuit. This phenomenon is called ‘mutual induction’.
or The phenomenon of producing an induced emf in a coil due to the change in current in the other coil is known as mutual induction.
Coefficient of mutual induction (M)-
If two coils (P-primary coil or coil 1, S-Secondary Coil or coil 2) are arranged as shown in the below figure.
If we change the current through the coil P (i.e $i_1$ ) then flux passing through Coil S (i.e $\phi_2$ ) will change.
I.e $N_2 \phi_2 \propto i_1 \Rightarrow N_2 \phi_2=M_{21} i_1=M i_1$
where
$M_{21}=$ mutual induction of Coil 2 w.r. t Coil 1
$N_1=$ Number of turns in the primary coil
$N_2=$ Number of turns in the secondary coil
$i_1=$ current through the primary coil or coil 1
Similarly, if we exchange the position of Coil 1 and Coil 2
then
If we change the current through the coil S (i.e $i_2$ ) then flux passing through Coil $\mathrm{P}\left(\mathrm{i} . \mathrm{e} \phi_1\right)$ will change.
I.e $N_1 \phi_1 \propto i_2 \Rightarrow N_1 \phi_1=M_{12} i_2=M i_2$
where
$M_{12}=$ mutual induction of Coil 1 w.r. 1 Coil 2
$N_1=$ Number of turns in the primary coil
$N_2=$ Number of turns in the secondary coil
$i_2=$ current through the coil 2 or Coils
- As $N_2 \phi_2=M i_1$
If $i_1=1 \mathrm{amp}, N_2=1$ then, $M=\phi_2$
I.e coefficient of mutual induction of two coils is numerically equal to the magnetic flux linked with one coil when unit current flows through the neighboring coil.
- Using Faraday Second Law of Induction emf we get
$
\varepsilon_2=-N_2 \frac{d \phi_2}{d t}=-M \frac{d i_1}{d t}
$
If $\frac{d i_1}{d t}=1 \frac{a m p}{s e c}$ and $N_2=1$ then $\left|\varepsilon_2\right|=M$
I.e The coefficient of mutual induction of two coils is numerically equal to the emf induced in one coil when the rate of change of current through the other coil is unity.
Units and dimensional formula of ‘M’-
S.I. Unit - Henry (H)
And
$
1 H=\frac{1 V \cdot s e c}{A m p}
$
And its dimensional formula is $M L^2 T^{-2} A^{-2}$
Dependence of mutual inductance
- Number of turns $\left(\mathrm{N}_1, \mathrm{~N}_2\right)$ of both coils
- Coefficient of self inductances $\left(L_1, L_2\right)$ of both the coils
and the relation between $M, L_1, L_2$ is given as
$
M=K \sqrt{L_1 L_2}
$
where $\mathrm{K}=$ coeffecient of coupling.
If $\mathrm{L}=0$ then $\mathrm{M}=0$
If $\mathrm{K}=0$ i.e case of No coupling then $\mathrm{M}=0$.
- Distance(d) between two coils (i.e As dincreases then $M$ decreases)
- The magnetic permeability of medium between the coils $\left(\mu_r\right)$
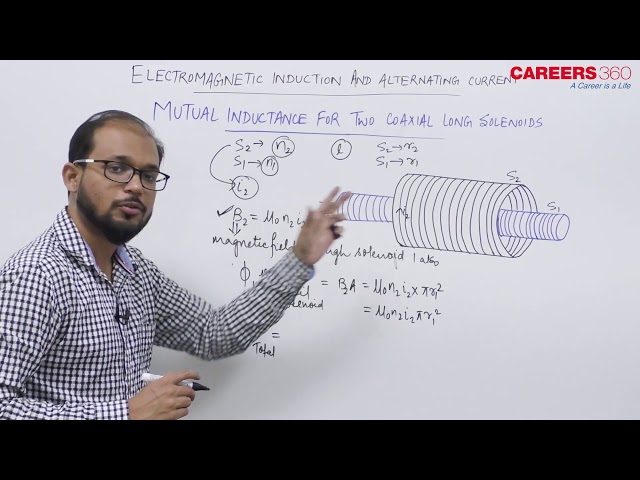
Consider two long co-axial solenoids of the same length $l$. Let $A_1$ and $A_2$ be the area of the cross-section of the solenoids with $A_1$ being greater than $A_2$ as shown in the below figure.

The turn density of these solenoids are $n_1$ and $n_2$ respectively are given as
$
n_1=\frac{N_1}{l} \text { and } n_2=\frac{N_2}{l}
$
Let $i_1$ be the current flowing through solenoid 1 , then the magnetic field produced inside it is given as
$
B_1=\mu_o n_1 i_1
$
As the field lines of $\overrightarrow{B_1}$ are passing through the area $A_2$
So the magnetic flux linked with each turn of solenoid 2 due to solenoid 1 and is given by
$
\Phi_{21}=\int_{A_2} \bar{B}_1 \cdot d \vec{A}=B_1 A_2=\left(\mu_0 n_1 i_1\right) A_2
$
The total flux linkage of solenoid 2 with total turns $N_2$ is
$
\begin{aligned}
& \left(\phi_{21}\right)_{\text {total }}=N_2 \Phi_{21}=\left(n_2 l\right)\left(\mu_0 n_1 i_1\right) A_2 \\
& \Rightarrow\left(\phi_{21}\right)_{\text {total }}=N_2 \Phi_{21}=\left(\mu_0 n_1 n_2 A_2 l\right) i_1
\end{aligned}
$
And Using $\left(\phi_{21}\right)_{\text {total }}=N_2 \Phi_{21}=M_{21} i_1$ we get
$
M_{21}=\mu_0 n_1 n_2 A_2 l
$
Where $M_{21}$ is the mutual inductance of the solenoid 2 with respect to solenoid 1.
Similarly ${M}_{12}=$ mutual inductance of solenoid 1 with respect to solenoid 2 is given as
$
M_{12}=\mu_0 n_1 n_2 A_2 l
$
Hence $M_{21}=M_{12}=M$
So, In general, the mutual inductance between two long co-axial solenoids is given by
$
M=\mu_0 n_1 n_2 A_2 l
$
If a dielectric medium of permeability $\mu$ is present inside the solenoids, then
$
\mathrm{M}=\mu \mathrm{n}_1 \mathrm{n}_2 \mathrm{~A}_2 \mathrm{l} \quad \text { or } \quad \mathrm{M}=\mu_0 \mu_{\mathrm{r}} \mathrm{n}_1 \mathrm{n}_2 \mathrm{~A}_2 \mathrm{l}
$
Consider two circular coils one of radius 'r1' and the other of radius' r2'placed coaxially with their centers coinciding as shown in the below figure.

Since $r_1 \gg \gg>r_2$ so we can assume coil 2 is at the center of coil 1 .
If
Suppose a current $i_1$ flows through the outer circular coil. Then Magnetic field at the center of the coil 1 is given as
$
B_1=\frac{\mu_0 N_1 i_1}{2 r_1}
$
So the total flux passing through coil 2 will be given as
$
\left(\phi_2\right)_{\text {total }}=N_2 B_1 A_2=\frac{\mu_0 N_1 N_2 i_1 A_2}{2 r_1}
$
And using $\left(\phi_2\right)_{\text {total }}=M i_1$
$
\text { we get } M=\frac{\mu_0 N_1 N_2 A_2}{2 r_1}=\frac{\mu_0 N_1 N_2\left(\pi r_2^2\right)}{2 r_1}
$
Where $\mathrm{M}=$ mutual inductance between two concentric coils
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"