Methods of Determining Reaction Order - Practice Questions & MCQ
Quick Facts
-
14 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
The variation of the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction with substrate concentration is correctly represented by graph
Which among the following graphs pertain to a zero order reaction?
For a reaction A + B → products, the rate of reaction was doubled when concentration of A was doubled. When concentration of A and B both was doubled, the rate was again doubled, order of reaction with respect to A and B are respectively -
JEE Main 2026: January Question Paper with Solutions
JEE Main 2026 Tools: College Predictor
JEE Main 2026: Important Formulas | Foreign Universities in India
Consider the reaction :
$
\mathrm{C}_{2(a q)}+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~S}_{(a q)} \longrightarrow \mathrm{S}_{(5)}+2 \mathrm{H}_{(2 q)}^{+}+2 \mathrm{C}_{(2 q)}^{-}
$
The rate of reaction for this reaction is
$
\text { Rate }=K\left[\mathrm{Cl}_2\right]\left[\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~S}\right]
$
Which of these mechanism is/are consistent with this rate equation ?
A $\mathrm{Cl}_2+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~S} \rightarrow \mathrm{H}^{+}+\mathrm{Cl}^{-}+\mathrm{Cl}^{+}+\mathrm{HS}^{-}$(slow)
$
\mathrm{Cl}^{+}+\mathrm{HS}^{-} \rightarrow \mathrm{H}^{+}+\mathrm{Cl}^{-}+S(\text { fast })
$
B $H_2 S \Leftrightarrow H^{+}+H S^{-}$(fast equilibrium $)$
$
\mathrm{Cl}_2+\mathrm{HS}^{-} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{Cl}^{-}+\mathrm{H}^{+}+\mathrm{S}(\text { Slow })
$
Concepts Covered - 3
It is used when the rate law involves only one concentration term.
$\mathrm{t}_{1 / 2} \propto(\mathrm{a})^{1-\mathrm{n}}$
or $\mathrm{t}_{1 / 2} \propto 1 / \mathrm{a}^{\mathrm{n}-1}$
For two different concentrations, we have:
$\frac{\left(\mathrm{t}^{1 / 2}\right)_1}{\left(\mathrm{t}^{1 / 2}\right)_2}=\left(\frac{\mathrm{a}_2}{\mathrm{a}_1}\right)^{\mathrm{n}-1}$
On taking logarithms on both sides, we get:
$\log _{10} \frac{\left(\mathrm{t}_{1 / 2}\right)_1}{\left(\mathrm{t}_{1 / 2}\right)_2}=(\mathrm{n}-1) \log _{10}\left(\mathrm{a}_2 / \mathrm{a}_1\right)$
Hence,
$\mathrm{n}=1+\frac{\log \left(\mathrm{t}^{1 / 2}\right)_1-\log \left(\mathrm{t}^{1 / 2}\right)_2}{\log \mathrm{a}_2-\log \mathrm{a}_1}$
Here, n is the order of the reaction.
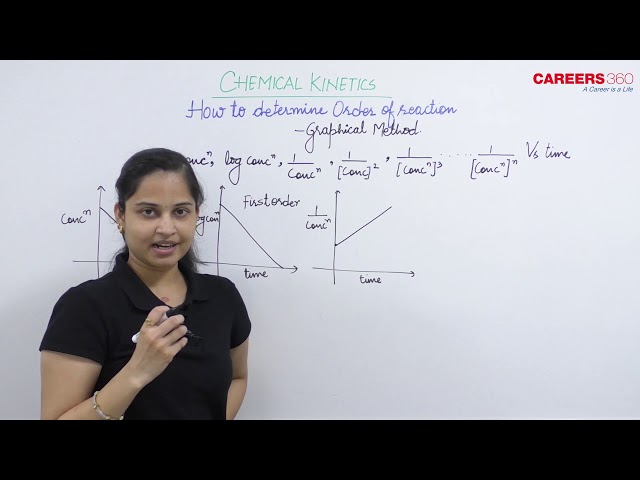
Here graphs are plotted between rate and concentration to find the order of the reaction.
$\left[\right.$ Rate $\left.=\mathrm{k}(\text { concentration })^{\mathrm{n}}\right]$
Plots of Rate vs Concentration

If the data for time(t) and [A] is given then this method is applicable. Thus follows the steps given below to find the order of reaction by using the integrated rate law method.
- Check for First Order:
- Use the formula given below to find out the two values of k as k1 and k2.$\mathrm{k}=\frac{2.303}{\mathrm{t}} \log _{10}\left[\frac{\mathrm{~A}_{\mathrm{o}}}{\mathrm{A}}\right]$
- If these two values k1 and k2 are same, then this given reaction is of first-order. But if k1≠ k2, then check for zero-order.
- Check for Zero-Order:
- Use the formula given below to find out the two values of k as k1 and k2.$\mathrm{k}=\frac{\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{o}}-\mathrm{A}}{\mathrm{t}}$
- Again, if these two values k1 and k2 are same, then this given reaction is of zero-order. But if k1≠ k2, then check for second-order.
- Check for Third-Order:
- Use the formula given below to find out the two values of k as k1 and k2.$\mathrm{k}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{t}}\left[\frac{1}{\mathrm{~A}}-\frac{1}{\mathrm{~A}_{\mathrm{o}}}\right]$
- Further, if these two values k1 and k2 are same, then this given reaction is of second-order. But if k1≠ k2, then check for third-order and so on.
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"