Equation of The Plane Bisecting the Angle Between Two Planes - Practice Questions & MCQ
Quick Facts
-
Equation of The Plane Bisecting the Angle Between Two Planes is considered one of the most asked concept.
-
12 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
Find the equation of plane bisecting the angle b/w the plane $r.\left(\widehat{i}-2\widehat{j}+3\widehat{k}\right)\:=\:5\:\:and\:\:r.\left(\widehat{i}-2\widehat{j}+3\widehat{k}\right)\:=3$
Concepts Covered - 1
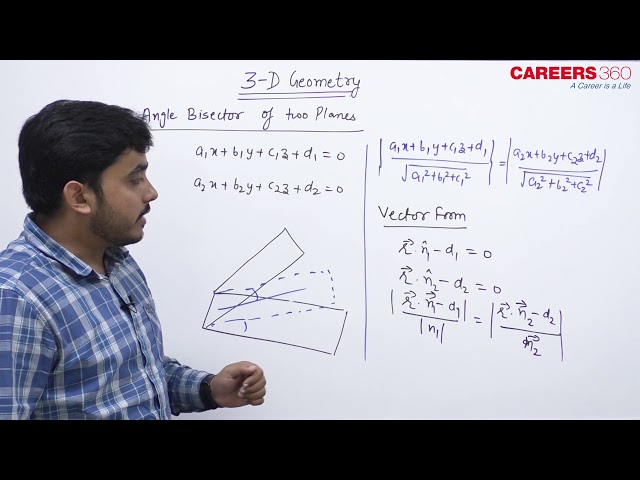
Cartesian Form
Equation of the planes bisecting the angle between the planes a1x + b1y + c1z + d1 = 0 and a2x + b2y + c2z + d2 = 0 is
$
\frac{a_1 x+b_1 y+c_1 z+d_1}{\sqrt{a_1^2+b_1^2+c_1^2}}= \pm \frac{a_2 x+b_2 y+c_2 z+d_2}{\sqrt{a_2^2+b_2^2+c_2^2}}
$
Proof:
Given planes are
$
\begin{array}{ll}
& a_1 x+b_1 y+c_1 z+d_1=0 \\
\text { and } & a_2 x+b_2 y+c_2 z+d_2=0
\end{array}
$
Let P(x, y, z) be a point on the plane bisecting the angle between planes (i) and (ii).
Let PL and PM be the length of perpendiculars from P to planes (i) and (ii).

$\begin{array}{rlrl}\therefore & P L & =P M \\ \Rightarrow & & \left|\frac{a_1 x+b_1 y+c_1 z+d_1}{\sqrt{a_1^2+b_1^2+c_1^2}}\right| & =\left|\frac{a_2 x+b_2 y+c_2 z+d_2}{\sqrt{a_2^2+b_2^2+c_2^2}}\right| \\ \frac{a_1 x+b_1 y+c_1 z+d_1}{\sqrt{a_1^2+b_1^2+c_1^2}} & = \pm \frac{a_2 x+b_2 y+c_2 z+d_2}{\sqrt{a_2^2+b_2^2+c_2^2}}\end{array}$
This is an equation of planes bisecting the angles between the planes (i) and (ii).
Vector Form
Equation of the planes bisecting the angle between the planes $\overrightarrow{\mathbf{r}} \cdot \overrightarrow{\mathbf{n}}=d_1$ and $\overrightarrow{\mathbf{r}} \cdot \overrightarrow{\mathbf{n}}_2=d_2$ is
$
\left|\frac{\overrightarrow{\mathbf{r}} \cdot \overrightarrow{\mathbf{n}}_1-d_1}{\overrightarrow{\mathbf{n}}_1}\right|=\left|\frac{\overrightarrow{\mathbf{r}} \cdot \overrightarrow{\mathbf{n}}_2-d_2}{\overrightarrow{\mathbf{n}}_2}\right|
$
Bisector of the Angle between the Two Planes Containing the Origin
Let the equation of the two planes be
$
\begin{array}{ll}
& a_1 x+b_1 y+c_1 z+d_1=0 \\
\text { and } & a_2 x+b_2 y+c_2 z+d_2=0
\end{array}
$
where $\mathrm{d}_1$ and $\mathrm{d}_2$ are positive.
Then the equation of the bisector of the angle between the planes (i) and (ii) containing the origin is
$
\frac{a_1 x+b_1 y+c_1 z+d_1}{\sqrt{a_1^2+b_1^2+c_1^2}}=\frac{a_2 x+b_2 y+c_2 z+d_2}{\sqrt{a_2^2+b_2^2+c_2^2}}
$
Bisector of the Acute and Obtuse Angle between Two Planes
Let the equation of the two planes be
and
$
\begin{aligned}
& a_1 x+b_1 y+c_1 z+d_1=0 \\
& a_2 x+b_2 y+c_2 z+d_2=0
\end{aligned}
$
1. If $a_1 a_2+b_1 b_2+c_1 c_2>0$, then the equation of the bisector of the obtuse angle is,
$
\frac{\mathrm{a}_1 \mathrm{x}+\mathrm{b}_1 \mathrm{y}+\mathrm{c}_1 \mathrm{z}+\mathrm{d}_1}{\sqrt{\mathrm{a}_1^2+\mathrm{b}_1^2+\mathrm{c}_1^2}}=\frac{\mathrm{a}_2 \mathrm{x}+\mathrm{b}_2 \mathrm{y}+\mathrm{c}_2 \mathrm{z}+\mathrm{d}_2}{\sqrt{\mathrm{a}_2^2+\mathrm{b}_2^2+\mathrm{c}_2^2}}
$
2. If $a_1 a_2+b_1 b_2+c_1 c_2<0$, then the equation of the bisector of the obtuse angle is,
$
\frac{\mathrm{a}_1 \mathrm{x}+\mathrm{b}_1 \mathrm{y}+\mathrm{c}_1 \mathrm{z}+\mathrm{d}_1}{\sqrt{\mathrm{a}_1^2+\mathrm{b}_1^2+\mathrm{c}_1^2}}=-\frac{\mathrm{a}_2 \mathrm{x}+\mathrm{b}_2 \mathrm{y}+\mathrm{c}_2 \mathrm{z}+\mathrm{d}_2}{\sqrt{\mathrm{a}_2^2+\mathrm{b}_2^2+\mathrm{c}_2^2}}
$
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"