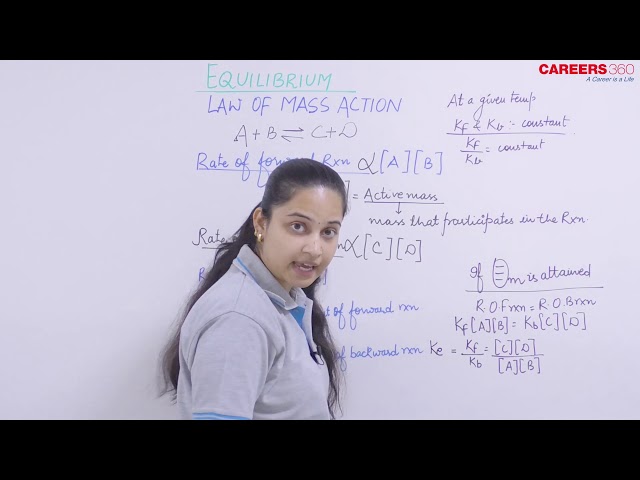Law Of Mass Action - Practice Questions & MCQ
Quick Facts
-
7 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
28 g N2 and 6 g H2 were mixed. At equilibrium 17 g NH3 was formed. The mass of N2 and H2 of equilibrium are
Concepts Covered - 1
It was introduced by Guldberg and Waage. It states that “the rate at which a substance reacts is directly proportional to its activity and the rate at which substances react together is directly proportional to the product of their activity each raised to a power which is equal to the corresponding stoichiometric number the substance present in the chemical reaction".
Activity is generally represented in terms of concentration or pressure of species involved
If active masses of A, B, C and D be represented in terms of their concentrations [A], [B], [C] and [D] respectively, then:
Rate of reaction of A ∝ [A]m
Rate of reaction of B ∝ [B]n
R1 ∝ [A]m [B]n = K1 [A]m[B]n
R2 ∝ [C]p [D]q = K2 [C]p [D]q
NOTE: For pure solids or pure liquids , activity is always unity (1) .
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"