Depression in Freezing Point - Practice Questions & MCQ
Quick Facts
-
Depression in Freezing Point is considered one of the most asked concept.
-
36 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
In the depression of freezing point experiment
A. Vapour pressure of the solution is less than that of pure solvent
B. Vapour pressure of the solution is more than that of pure solvent
C. Only solute molecules solidify at the freezing point
D. Only solvent molecules solidify at the freezing point
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Assuming same molality & 100% dissociation which solution has minimum depression in freezing point?
The solution from the following with highest depression in freezing point/lowest freezing point is
JEE Main 2026: Result OUT; Check Now | Final Answer Key Link
JEE Main 2026 Tools: College Predictor
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Link | Foreign Universities in India
Correct expression for molal freezing point depression constant Kf will be:
Which is the cheapest anti freezing reagent used in car radiator (per kg price of each is same)?
1gm of non-electrolyte solute disolved in 50gm of benzene lowered the freezing point of benzene by 0.4 K. Freezing point depression constant of benzene is 5.12 K Kg/mol. Molar mass of solute is
Concepts Covered - 1
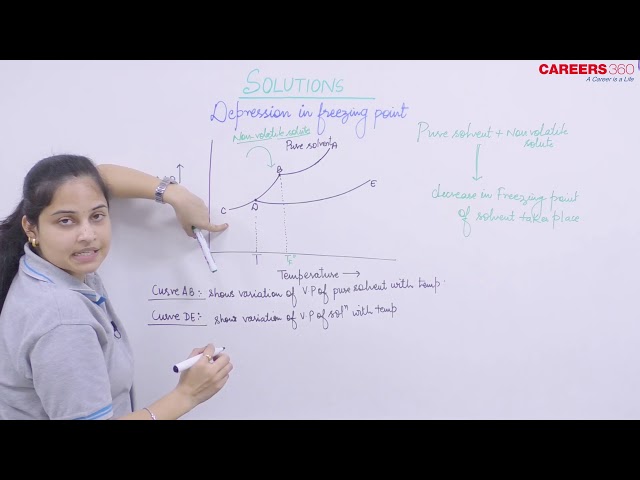
Depression in Freezing Point:
Freezing Point: It is the temperature at which the liquid and the solid form of the same substance are in equilibrium and have the same vapour pressure. A solution freezes when its vapour pressure is equal to the vapor pressure of pure solid solvent. Due to lower vapour pressure of the solution, solid form of a solution separates out a lower temperature.
On adding a non-volatile solute to the solvent, the vapor pressure of the solution is lesser than the solvent and the vapor pressure of the solution becomes equal to the vapor pressure of solid solvent at a lower temperature when compared to the pure solvent and hence the freezing point of decreases.
Suppose are the freezing point of pure solvent and solution respectively. Decrease in freezing point
is given as:

- This is also termed as cryoscopy and depression of freezing point
- For a dilute solution,
is directly proportional to the molality (m) of the solution.
Hence
If molality of the solution is one, then
and M can be found out by using these relations.
Here w = weight of solute
W = weight of solvent
Kf = molal depression constant or cryoscopic constant.
M = molar mass of solute
M1 = molar mass of solvent
The value of Kf or Cryoscopic constant is a property of the solvent only and does not depend on the type of solute. The value of Kf can be calculated as:
Here,
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"