Mendeleev’s Periodic table - Practice Questions & MCQ
Quick Facts
-
9 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
If a diagonal line is drawn in Mendeleev's periodic table from left to bottom right, the elements below the diagonal will be:
Concepts Covered - 1
Dmitri Mendeleev:
Mendeleev proposed the Periodic Law and constructed his Periodic Table of elements. At that time, the structure of atoms was unknown and Mendeleev’s idea to consider that the properties of the elements were in some way related to their atomic masses was a very imaginative one. To place certain elements into the correct group from the point of view of their chemical properties, Mendeleev reversed the order of some elements as they did not fit the scheme classification if the order of atomic weights has strictly followed. Mendeleev also had the foresight to leave gaps in the Periodic Table for elements unknown at that time and predict their properties from the trends that he observed among the properties of related elements. Mendeleev’s predictions were proved to be astonishingly correct when these elements were discovered later. Mendeleev’s Periodic Law spurred several areas of research during the subsequent decades.
MENDELEEV'S PERIODIC TABLE:
-
Mendeleev's periodic law: The physical and chemical properties of elements are the periodic function of their atomic weight
-
Characteristic of Mendeleev's periodic table :
-
It is based on atomic weight
-
63 elements were known, noble gases were not discovered.
-
He was the first scientist to classify the elements in a systematic manner i.e. in horizontal rows and in vertical columns.
-
Horizontal rows are called periods and there were 7 periods in Mendeleev's Periodic table.
-
Vertical columns are called groups and there were 8 groups in Mendeleev's Periodic table.
-
Each group upto VIIth is divided into A & B subgroups.'A' sub groups elements are called normal elements and 'B' sub groups elements are called transition elements.
-
The VIIIth group was consisting of 9 elements in three rows (Transitional metals group).
-
The elements belonging to the same group exhibit similar properties.
-
-
Merits or Advantages of Mendeleev's periodic table :
- Study of elements: First time all known elements were classified into groups according to their similar properties. So study of the properties of elements becomes easier.
-
Prediction of new elements: It gave encouragement to the discovery of new elements as some gaps were left in it.
Sc (Scandium) Ga (Gallium) Ge (Germanium) Tc (Technetium)
These were the elements for whom position and properties were well defined by Mendeleev even before their discoveries and he left the blank spaces for them in his table.
Ex. Blank space at atomic weight 72 in silicon group was called Eka silicon (means properties like silicon) and element discovered later was named Germanium.
Similarly, other elements discovered after Mendeleev periodic table was.
Eka aluminium – Gallium(Ga)
Eka Boron – Scandium (Sc)
Eka Silicon – Germanium (Ge)
Eka Manganese – Technetium (Tc)
3. Correction of doubtful atomic weights: Correction was done in the atomic weight of some elements.
Atomic weight = Valency × Equivalent weight.
Initially, it was found that the equivalent weight of Be is 4.5 and it is trivalent (V = 3), so the weight of Be was 13.5 and there is no space in Mendeleev's table for this element. So, after correction, it was found that Be is actually divalent (V = 2). So, the weight of Be became 2 × 4.5 = 9 and there was a space between Li and B for this element in Mendeleev's table.
– Corrections were done in atomic weight of elements are – U, Be, In, Au, Pt.
-
Defects of Mendeleev's Periodic Table:
-
The position of hydrogen is uncertain. It has been placed in lA and VII-A groups because of its resemblance with both the groups.
-
No separate positions were given to isotopes.
-
It is not clear whether the lanthanides and actinides are related to IIA or IIB group.
-
Although there is no resemblance except valency of subgroups A and B, they have been put in the same group.
-
Order of increasing atomic weights is not strictly followed in the arrangement of elements in the periodic table. For e.g. – Co (At. wt. 58.9) is placed before I (127) and Ar (39.9) before K (39).
-
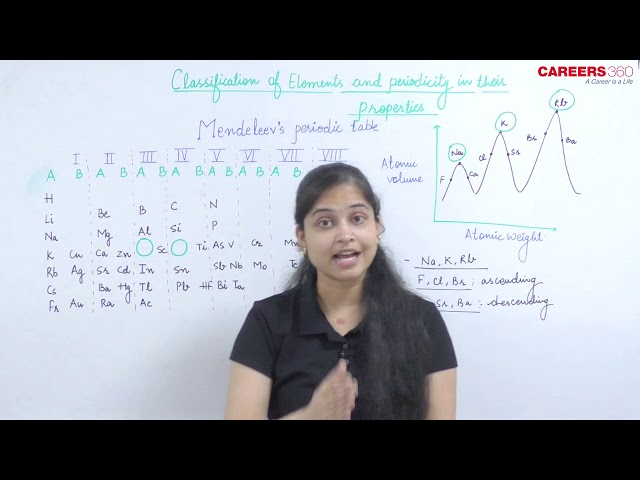
Lother Meyer:
-
He plotted a curve between atomic weight and the atomic volume of different elements.
-
The following observations can be made from the curve –
-
Most electropositive elements i.e. alkali metals (Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs etc.) occupy the peak positions on the curve.
-
Less electropositive i.e. alkali earth metals (Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba) occupy the descending position on the curve.
-
Metalloids (B, Si, As, Te, At etc.) and transition metals occupy the bottom part of the curve.
-
Most electronegative i.e. halogens (F, Cl, Br, I) occupy the ascending position on the curve.
-
Note: Elements having similar properties occupy similar positions on the curve.
Conclusion: On the basis of this curve Lother Meyer proposed that the physical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic wt. and this becomes the base of Mendeleev's periodic table.

Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"