Electric Dipole - Practice Questions & MCQ
Quick Facts
-
29 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
An electric dipole is placed in an electric field generated by a point charge.
An electric dipole is kept in a non-uniform electric field. It experiences
Electric charges $q, q,-2 q$ are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle ABC of side l. The magnitude of the electric dipole moment of the system is
JEE Main 2026: Result OUT; Check Now | Final Answer Key Link
JEE Main 2026 Tools: College Predictor
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Link | Foreign Universities in India
The electric field at a point on the axis of an electric dipole depends on the distance r from dipole as :
The magnitude of the charge of an electric dipole is 3.2 x 10-19 C and the distance between them is 2Å. Then dipole moment is (in cm):
Concepts Covered - 1
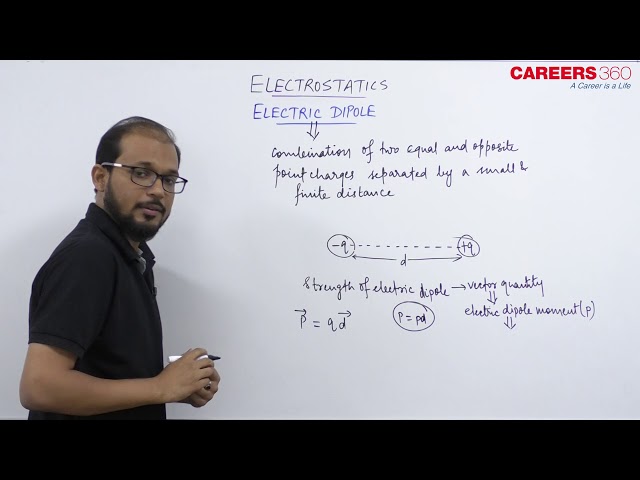
An electric dipole is a system of two equal and opposite point charges separated by a very small and finite distance.
Below is the figure showing an electric dipole consisting of two equal and opposite point charges $-q$ and $+q$ separated by a small distance $2 l$.

Dipole moment- The strength of an electric dipole is measured by a vector quantity known as electric dipole moment. Its magnitude is equal to the product of the magnitude of either charge and the distance between the two charges,
i.e. for the dipole, as shown in the above figure dipole moment is given as
$
(\vec{P})=q(\overrightarrow{2 l})
$
And its direction is along the line from $-q$ to $+q$.
Its $\mathrm{S} . \mathrm{I}$ unit is C-m
and its cgs unit is Debye ( 1 Debye $\left.=3.3 \times 10^{-30} \mathrm{C}-\mathrm{m}\right)$
The axial line of dipole- A line passing through the negative and positive charges of the electric dipole is called the axial line of the electric dipole.
Centre of dipole- The midpoint of the line joining the two charges is called the centre of the dipole.
Equatorial line- An equatorial line of a dipole is the line perpendicular to the axis of the dipole and passing through the Centre of the dipole.
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"