Properties Of Interstitial Compounds - Practice Questions & MCQ
Quick Facts
-
10 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
Which of the following is not a property of interstitial compounds -
Calomel $\left(\mathrm{Hg}_2 \mathrm{Cl}_2\right)$ on reaction with ammonium hydroxide gives
Interstitial compounds are formed when small atoms are trapped inside the crystal lattice of metals. Which of the following is not the characteristic property of interstitial compounds?
JEE Main 2026: January Question Paper with Solutions
JEE Main 2026 Tools: College Predictor
JEE Main 2026: Important Formulas | Foreign Universities in India
The incorrect statement about interstitial compounds is
A metal exists as an oxide with formula M0.96O. Metal M can exist as M+2 and M+3 in its oxide M0.96O. The percentage of M+3 in the oxide is nearly
Concepts Covered - 1
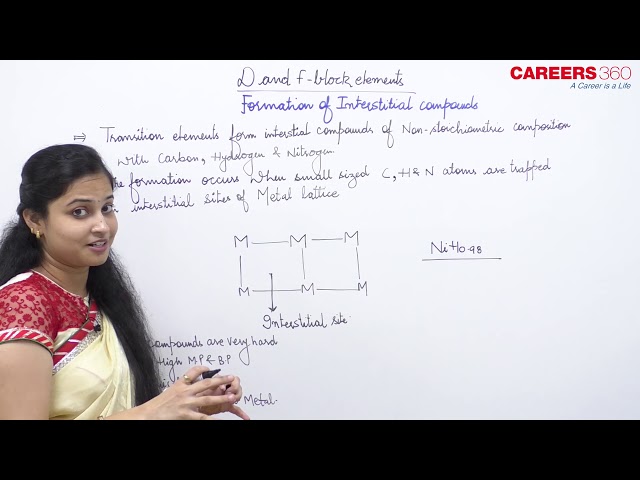
Interstitial compounds are those which are formed when small atoms like H, C or N are trapped inside the crystal lattices of metals. They are usually non stoichiometric and are neither typically ionic nor covalent, for example, TiC, Mn4N, Fe3H, VH0.56 and TiH1.7, etc. The formulas quoted do not, of course, correspond to any normal oxidation state of the metal. Because of the nature of their composition, these compounds are referred to as interstitial compounds. The principal physical and chemical characteristics of these compounds are as follows:
(i) They have high melting points, higher than those of pure metals.
(ii) They are very hard, some borides approach diamond in hardness.
(iii) They retain metallic conductivity.
(iv) They are chemically inert.
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"