Contact Angle - Practice Questions & MCQ
Quick Facts
-
7 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
When liquid is subjected to horizontal acceleration-
Two liquids A and B have $\theta_{\mathrm{A}}$ and $\theta_{\mathrm{B}}$ as contact angles in a capillary tube. If $K=\cos \theta_{\mathrm{A}} / \cos \theta_{\mathrm{B}}$, then identify the correct statement:
JEE Main 2026: Result OUT; Check Now | Final Answer Key Link
JEE Main 2026 Tools: College Predictor
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Link | Foreign Universities in India
Concepts Covered - 1
The shape of Liquid Meniscus-
-
When a capillary tube is dipped in a liquid, the liquid surface becomes curved near the point of contact. The curved surface of the liquid is called the meniscus of the liquid.
This curved surface is due to the resultant of two forces i.e. the force of cohesion and the force of adhesion.
-
If liquid molecule A is in contact with solid (i.e. wall of capillary tube) then forces acting on molecule A are
-
Force of adhesion $\left(F_a\right)$
This is force due to solid molecules on liquid molecules.
Here it will act outwards at a right angle to the wall of the tube.|
2. Force of cohesion $\left(F_c\right)$This is force due to liquid molecules on liquid molecules.
Here it will act at an angle $45^{\circ}$ to the vertical and towards liquid.
So the resultant force $\left(F_N\right)$ will be given by$
\overrightarrow{F_N}=\vec{F}_a+\vec{F}_c
$
And If $F_N$ makes an angle $\alpha$ with $F_a$Then
$
\tan \alpha=\frac{F_c \operatorname{Sin}(135)}{F_a+F_c \operatorname{Cos}(135)}=\frac{F_c}{\sqrt{2} F_a-F_c}
$
As we know that the free surface of the liquid adjusts itself at a right angle to this resultant force.
So by knowing the direction of resultant force we can find out the shape of the meniscus.
3. Shape of Liquid Meniscus in various cases.Case I- When $F_c=\sqrt{2} F_a$
As shown in the below figure
The resultant force acts vertically downwards.
Hence the liquid meniscus must be horizontal.
Example-Pure water in a silver-coated capillary tube.

Case II- $F_c<\sqrt{2} F_a$
As shown in the below figure
The resultant force is directed outside the liquid. Hence the liquid meniscus must be concave upward.
Example-Example: Water in glass capillary tube.

Case III- $F_c>\sqrt{2} F_a$
As shown in the below figure
The resultant force is directed inside the liquid. Hence the liquid meniscus must be convex upward.
Example: Mercury in glass capillary tube.

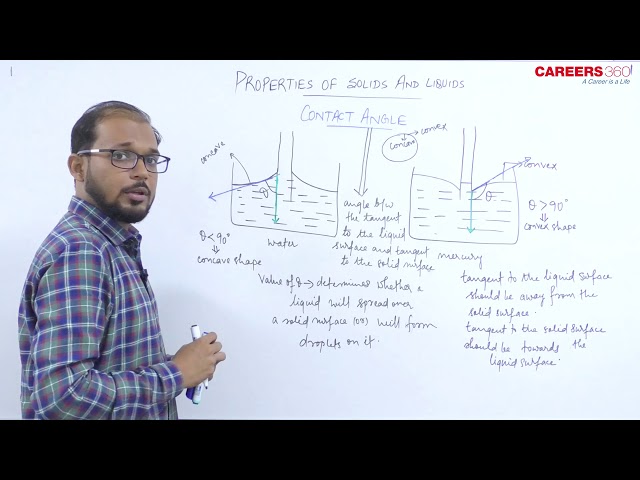
The angle of Contact $(\theta)$.
The angle of contact between a liquid and a solid is defined as the angle enclosed between the tangents to the liquid surface and the solid surface inside the liquid.
While drawing tangent keeps following things in mind.
1. Both the tangents being drawn at the point of contact of the liquid with the solid.
2. Tangent to the liquid surface should be away from the solid surface.
3. Tangent to the solid surface should be towards the liquid surface.
- Its value lies between $0^{\circ}$ and $180^{\circ}$
- When $F_c=\sqrt{2} F_a$ then $\theta=90^{\circ}$
i.e plane meniscus.
In this case, Liquid does not wets the solid surface

- When $F_c<\sqrt{2} F_a$ then $\theta<90^{\circ}$
i.e concave meniscus.
In this case, Liquid wets the solid surface

- When $F_c>\sqrt{2} F_a$ then $\theta>90^{\circ}$
i.e Convex meniscus.
In this case, Liquid does not wet the solid surface.

- On increasing the temperature, angle of contact decreases.
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"