Bomb Calorimeter - Practice Questions & MCQ
Quick Facts
-
4 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
X g of ice at 0 0C is added to 340 g of water at 20 0C. The final temperature of the resultant mixture is 5 0C. The value of X (in g ) is closed to
[ Heat of fusion of ice = 333 J/ g; Specific heat of water = 4.184 J/g.K ]
Concepts Covered - 1
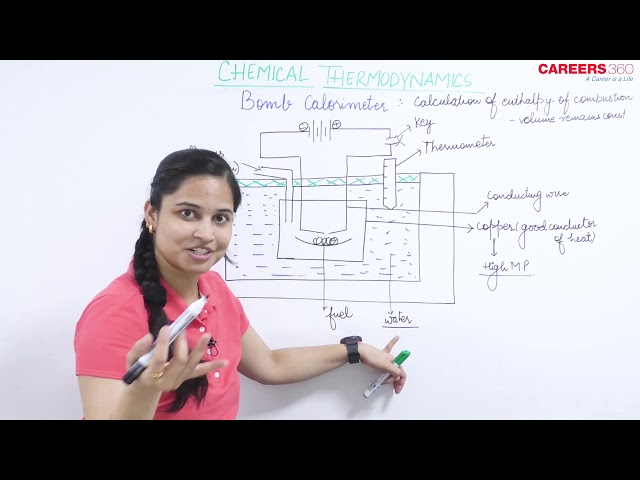
In the laboratory, the heat released during combustion is measured in a bomb calorimeter.
It consists of an insulated vessel containing water and a rigid, constant volume container (called bomb) inside it.
The combustion process is carried out isochorically in the bomb and the heat released during combustion is trapped in the vessel and is used to raise the temperature of the calorimeter system.
The change in temperature can be measured with the help of thermometer and knowing the heat capacity of the system, the heat released due to combustion can be calculated.
Suppose T1 and T2 are initial and final temperatures and C be the heat capacity of the system, then
$\mathrm{Q}=\mathrm{C}\left(\mathrm{T}_2-\mathrm{T}_1\right)$
Now, since the combustion occurs in the rigid bomb, therefore the heat liberated is at constant volume and thus knowing the amount of substance undergoing combustion, the internal energy change during combustion can be calculated.
- If 1 mole of substance undergoes combustion then
$\mathrm{Q}=|\Delta \mathrm{E}|=\mathrm{C}\left(\mathrm{T}_2-\mathrm{T}_1\right)$
- If x g of substance (molar mass M) undergoes combustion then
$\mathrm{Q}=|\Delta \mathrm{E}| \times \frac{\mathrm{w}}{\mathrm{M}}=\mathrm{C}\left(\mathrm{T}_2-\mathrm{T}_1\right)$
Once, the value of $\Delta \mathrm{E}$ is calculated, we can calculate the $\Delta \mathrm{H}$ of the reaction using the following relation:
$\Delta \mathrm{H}=\Delta \mathrm{E}+\left(\Delta \mathrm{n}_{\mathrm{g}}\right) \mathrm{RT}$
The pictorial representation of a calorimeter system is given below

Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"