Detection Of Amplitude Modulated Wave - Practice Questions & MCQ
Quick Facts
-
19 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
pulse position modulation is defined as
pulse width modulation is defined as
Concepts Covered - 1
Detection of Amplitude Modulated Wave
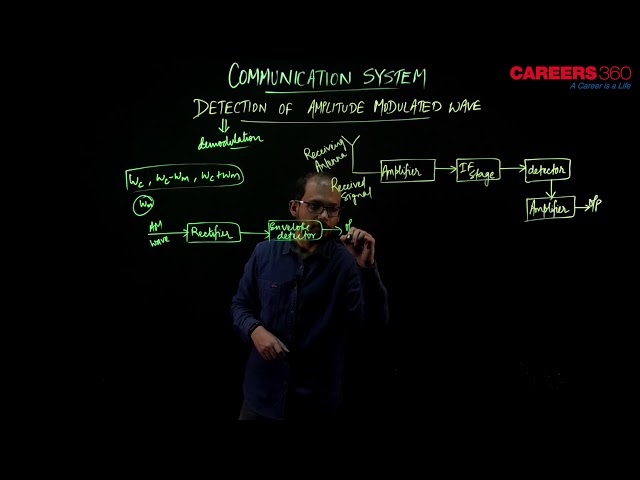
The transmitted message gets attenuated in propagating through the channel. The receiving antenna is, therefore, to be followed by an amplifier and a detector. In addition, to facilitate further processing, the carrier frequency is usually changed to a lower frequency by what is called an intermediate frequency (IF) stage preceding the detection. The detected signal may not be strong enough to be made use of and hence is required to be amplified. A block diagram of a typical receiver is shown in fig. below

Detection is the process of recovering the modulating signal from the modulated carrier wave. We just saw that the modulated carrier wave contains the frequencies $\omega_c$ and $\omega_c \pm \omega_m$. In order to obtain the original message signal $\mathrm{m}(\mathrm{t})$ of angular frequency $\omega_m$, a simple method is shown in the form of a block diagram below-

The modulated signal of the form given in the above figure (a) is passed through a rectifier to produce the output shown in (b). This envelope of a signal (b) is the message signal. In order to retrieve m(t), the signal is passed through an envelope detector.
So the detector actually removes these frequencies from the signal using diodes for an analog signal or uses digital means to obtain the natural frequency of the signal. Thus the detector generates the original frequency of the signal.
An important point to note is that in the above process a simple RC circuit can be additionally used along with the detector to generate the original frequency of the signal. This is known as a Detector Envelope which can be used to differentiate the incoming signal from the IF stage signal.
Limitation of amplitude modulation-
(1) Noisy reception
(2) Low efficiency
(3) Small operating range
(4) Poor audio quality
Some types of amplitude modulation-
- Pulse amplitude modulation (PAM)-The amplitude of the pulse varies in accordance with the modulating signal
- Pulse width modulation (PWM)-The pulse duration varies in accordance with the modulating signal.
- Pulse position modulation (PPM)-The position of the pulses of the carrier wave train is varied in accordance with the instantaneous value of the modulating signal.
Frequency modulation-
- Frequency modulation deviation-The The amount by which carrier frequency is varied from its unmodulated value.
The deviation is made proportional to the instantaneous value of the modulating voltage.
- Value of frequency deviation $=\delta=f-f_c$
$
\begin{aligned}
& d_{\max }=f_{\max }-f_c \\
& = \pm K E_m \\
& E_m=\text { modulating amplitude }
\end{aligned}
$
- The modulation index of frequency modulation-
It is defined as the ratio of maximum frequency deviation to the modulating frequency.
$
\begin{aligned}
& m_f=\frac{\delta_{\max }}{f_m} \\
& = \pm \frac{K E_m}{f_m}
\end{aligned}
$
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"